|
BUSINESS & POLITICS IN THE WORLD GLOBAL OPINION REPORT NO. 714 Week:
October 25 –October 31, 2021 Presentation:
November 05, 2021 PM
Modi’s Approval Rating Among Urban Indians Has Improved Since August 2021
From 53% To 58% A
Majority (55%) Of Sudanese “Disapprove” Or “Strongly Disapprove” Of Military
Rule In
Recent Pre-Election Surveys Support For The ANC Has Been Measured
Consistently Below 50% Britons
Are Most Likely To Expect Big Delays In Parcel Deliveries For Online Shopping
(58%) Three-Quarters
Of Britons Expect Halloween To Go Ahead As Normal This Year At
Least One In Five Women Haven’t Checked For Signs Of Breast Cancer In The
Last Year 51%
Of The Public Say They Would Be Personally Unwilling To Stop Flying For
Leisure 2022
Fifa World Cup: 62% Of French People Think The France Team Will Win In Qatar 37%
Of American Adults Say Spending On Police Should Stay About The Same COVID-19
Vaccine Now Required For 36% Of U.S. Workers Paypal
Is The Clear Leader With 72.5% Of Australians Aware Of The Platform Positive
Impact Of Intersectionality In Advertising In 4 Countries INTRODUCTORY NOTE 714-43-23/Commentary: 73% Of Employers In France Suffer From Poorly Mastered Written And
Oral Expression By Their Teams, All The More So In A Period Of Widespread
Teleworking Among the main lessons of the study
As
long-distance exchanges multiply and informal moments of communication become
rarer, expression and spelling skills are essential: precision,
disambiguation, conciseness are invaluable in avoiding misunderstandings.
In the
recruitment process, fluency in French is more important than fluency in
English This
statement sounds like a no-brainer. However, over the years of
globalization, a good level of English has been an undeniable advantage in
hiring. At a time when the internationalization of trade has come to a
halt, the employment passport has changed scope, and mastery of expression
and spelling has become a priority.
French language certification makes the difference with employers Aware of
these growing challenges, companies, higher education establishments and
schools encourage their employees, students or pupils to improve the quality
of their expression. To motivate them, display their progress, certify
their level, these players resort to certification in French, a possibility
still little known to the general public. A lever for employability?
(Ipsos France) October 26,
2021 714-43-24/Country Profile:
SUMMARY
OF POLLS
ASIA (India) PM
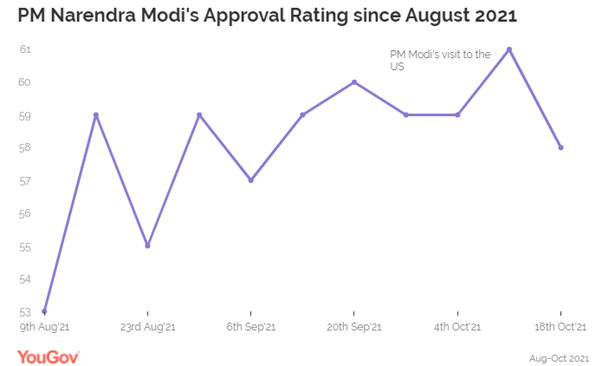
Modi’s Approval Rating Among Urban Indians Has Improved Since August 2021
From 53% To 58% YouGov’s political tracker, that tracks
public opinion on politics and government affairs in the country shows PM
Modi’s approval rating among urban Indians has improved since August 2021,
when we first started tracking this data, from 53% in the beginning of August
(9th August 2021) to 58% in October (18th October).
Approval for PM Modi is the highest among residents of North India- at 63%.
On the other hand, disapproval is the highest among South Indians (at 36%). (YouGov India) October 28, 2021 MENA (Iran) 86%
Of The Population Believe That Domestic Inefficiency And Corruption Have Had
The Worst Impact On The Iranian Economy’s Current State The survey titled “Iranians’ Attitudes
toward International Relations” was conducted September 21-30, 2021. Around
23 thousandrespondents participated in the study. The final sample used in
this report consisted of 20,097 Iranians
living inside Iran. This study’s findings reflect the views of literate Iranian residents aged above 19 or
85% of Iran’s adult population. The results can be generalized to
the target population with a 95% credibility level and credibility intervals
of 5%. (Gamaan) October 27, 2021 AFRICA (Sudan) A
Majority (55%) Of Sudanese “Disapprove” Or “Strongly Disapprove” Of Military
Rule A majority (55%) of Sudanese “disapprove”
or “strongly disapprove” of military rule. Even larger majorities reject
one-party rule (74%) and presidential dictatorship (71%).Half (50%) of
citizens prefer democracy to any other form of government – almost twice as
many as think that non-democratic systems of governance can be preferable in
some circumstances (28%). Opposition to rule by the military has increased by
9 percentage points since 2015. Disapproval of being governed by an
autocratic president or by a single political party has also increased (by 11
and 5 points, respectively). (Afrobarometer) 25 October 2021 (South
Africa) Unemployment
Is The Problem Mostly Widely Seen As A Top Priority For Government Action,
Cited By Six In 10 South Africans Unemployment is the problem mostly widely
seen as a top priority for government action, cited by six in 10 respondents
(60%). Job creation has been at the top of the list for the past decade.
Almost two-thirds (63%) of South Africans say they went without a cash income
at least once during the year preceding the survey, including 25% who did so
“many times” or “always.” Many also experienced frequent shortages of food
(14%), clean water (19%), medical care (13%), and cooking fuel (17%). (Afrobarometer) 26 October
2021 Only
About A Quarter (24%) South Africans Are Very Satisfied With The Party They
Voted For In The 2016 Local Government Election Research
recently undertaken by Ipsos, on behalf of the eNCA, revealed these and other interesting
findings about the South African electorate and prevailing opinions on local
government. Clearly, many of the current local authorities do not work
optimally or not at all for South African voters, as almost half (47%) of
those who are registered to vote on 1 November 2021, say they are very or
somewhat dissatisfied with the party they voted for in the 2016
local government election. (Ipsos South
Africa) 26 October
2021 In
Recent Pre-Election Surveys Support For The ANC Has Been Measured
Consistently Below 50% In recent pre-election surveys support for
the ANC has been measured consistently below 50% - a phenomenon not seen
commonly before. This is the most interesting finding in the eNCA/Ipsos pre-election series of opinion
surveys. Three waves of this study were conducted during October 2021. Since
the 1994 elections, results of both national and local government elections
have always returned the ANC with countrywide support well above
50%. (Ipsos South Africa) 31 October 2021 WEST
EUROPE (UK) Britons Are Most Likely To Expect Big Delays In Parcel
Deliveries For Online Shopping (58%) Britons are most likely to expect big
delays in parcel deliveries for online shopping (58%). This includes 17% who
consider it “very likely”. That being said, fewer Britons think it will
actually be harder to find Christmas presents this year (37%).Being unable to
give loved ones presents this year is one of the most upsetting prospects to
Britons, with 60% of people saying they would find this distressing. People
are far less bothered by the potential that they themselves would not receive
any gifts as a result of supply shortages, at just 27%. (YouGov UK) October 28, 2021 Three-Quarters Of Britons Expect Halloween To Go Ahead As
Normal This Year New research by Ipsos MORI shows high hopes
for Halloween fans in 2021 as 76% of Britons expect Halloween to be
celebrated as it normally would this year. This time last year, only 20%
thought it was likely to continue as usual. A similar proportion (77%) expect
households to mix freely. All Halloween activities look set to go
ahead, 10% say they will take a child trick-or-treating this year (10% say
they normally do this) while 11% will visit friends/family in another
household (10% normally) and 6% will go to a pub/restaurant (6% normally). (Ipsos MORI) 29 October 2021 At Least One In Five Women Haven’t Checked For Signs Of
Breast Cancer In The Last Year October marks breast cancer awareness
month. Despite being the most common cancer in the UK there is a
misconception among some that it only affects women. A new YouGov survey asks
both British men and women when, if ever, was the last time they did a
self-check, and if the disease has impacted their lives. Among women,
three quarters (76%) say they have ever checked themselves for signs of
breast cancer. This includes two in five (41%) who say they have done within
the last month, and 18% say they have done so in the last six months. Just
11% of women say they’ve never done so. (YouGov UK) October 29, 2021 51% Of The Public Say They Would Be Personally Unwilling To
Stop Flying For Leisure Indeed, 51% of the public say they would be
personally unwilling to stop flying for leisure, compared to 23% who are
willing to do so or already doing so. Further, 76% believe most other people
would be unwilling to make this change. This suggests that perceived
effectiveness may also be being driven by its personal lifestyle impact
and/or that the policy would be rejected by the public, rather than just its
potential impact on climate change. (YouGov UK) October 31, 2021 (France) 73% Of Employers In France
Suffer From Poorly Mastered Written And Oral Expression By Their
Teams, All The More So In A Period Of Widespread Teleworking Employers suffer from poorly mastered
written and oral expression by their teams, all the more so in a period of widespread
teleworking. French skills are essential in the eyes of recruiters, far ahead
of English proficiency. 8 out of 10 employers consider the gaps in French for
the professional development of their employees to be crippling. When
recruiting, 80% of employers consider the difficulties in expressing
themselves to be prohibitive, and 73% of employers consider the difficulties
in writing to be prohibitive. (Ipsos France) October 26, 2021 2022 Fifa World Cup: 62% Of French People Think The France
Team Will Win In Qatar The second edition of the Nations Football
League ended in style with the success of the Blues in the final against
Spain, a few months after its premature exit in the knockout stages of Euro
2020. “The competition must indeed find its place between the Euro and the
World Cup, because only 44% of aficionados agree to see in the League of
Nations a prestigious competition today. A finding that is improving
nonetheless among 16-24 year olds (57%). », Comments Damien Barnier, MSU
Research Director at Ipsos in France. (Ipsos France) October 27, 2021 NORTH AMERICA (USA) 37% Of American Adults Say Spending On Police Should Stay
About The Same Amid mounting public concern about violent
crime in the United States, Americans’ attitudes about police funding in
their own community have shifted significantly. The share of adults who say
spending on policing in their area should be increased now stands at 47%, up
from 31% in June 2020. That includes 21% who say funding for their local
police should be increased a lot,
up from 11% who said this last summer. (PEW) OCTOBER 26, 2021 Roughly One-In-Five Say That The Federal Government Should
Stop Enforcing The Separation Of Church And State (19%) Some Americans clearly long for a more
avowedly religious and explicitly Christian country, according to a March
2021 Pew Research Center survey. For instance, three-in-ten say public school
teachers should be allowed to lead students in Christian prayers, a practice
that the Supreme Court has ruled unconstitutional. Roughly one-in-five say
that the federal government should stop enforcing the separation of church
and state (19%) and that the U.S. Constitution was inspired by God (18%). And
15% go as far as to say the federal government should declare the U.S. a
Christian nation. (PEW) OCTOBER 28, 2021 COVID-19 Vaccine Now Required For 36% Of U.S. Workers The latest Gallup COVID-19 tracking survey
finds 36% of U.S. employees saying their employer is requiring all its
workers without a medical exemption to be vaccinated against COVID-19. The
percentage has steadily increased each of the last three months, rising from
9% in July. . Thirty-six percent of U.S. adults working full or part time say
their employer is requiring employees to get vaccinated against COVID-19. The
percentage is up from 29% in September and 19% in August. It ranged between
5% and 9% from May to July. (Gallup) OCTOBER 29, 2021 AUSTRALIA Paypal Is The Clear Leader With 72.5% Of Australians Aware
Of The Platform Of the four leading online payment platforms
PayPal is the clear leader with 72.5% of Australians aware of the platform.
This compares to just under a quarter, 23.6%, that are aware of Visa
Checkout, and just under one-in-six aware of Western Union (16.4%) or
masterpass (16.3%).Now 47.3% of Australians have used PayPal in the last 12
months, up nearly 10% points from 37.8% in February 2020 just before the
pandemic hit Australia – reversing the trend. (Roy Morgan) October 26 2021 ALP (54%) Increases Lead Over The L-NP (46%) As The Federal
Government Discusses “Net Zero” Carbon Dioxide Emissions ALP support has increased to 54% (up 1%
point since mid-October) cf. L-NP on 46% (down 1% point) on a two-party
preferred basis according to the latest Roy Morgan Poll on Federal voting
intention conducted over the last two weekends. The 1% point swing to the ALP
came after the governing Liberal and National parties have spent the last few
weeks ‘haggling’ about a change in policy for the Government to support a
target of “Net Zero” carbon dioxide emissions for Australia by 2050. (Roy Morgan) October 27 2021 MULTICOUNTRY STUDIES Positive Impact Of Intersectionality In Advertising In 4
Countries The report examines the impact of intersectionality in advertising across
four countries (Japan, Turkey, the United Kingdom, and the United
States) revealing that advertising
that represents people across a variety of social categorizations resonates
with all consumers. This marks the second instalment of the
‘Beyond Gender' study; the first report released in 2018 centred on how
gender intersects with cultural contexts and forms of discrimination in
Brazil, India, and South Africa. Convened by UN Women, the Unstereotype
Alliance is a thought- and action platform that seeks to eradicate harmful
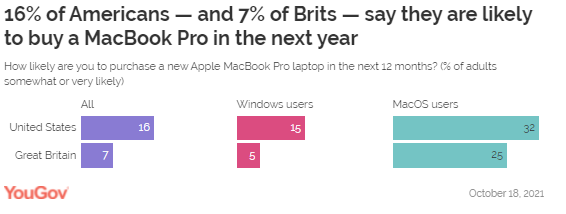
stereotypes from advertising and media. (Ipsos Denmark) 25 October 2021 Source: https://www.ipsos.com/en-dk/positive-impact-intersectionality-advertising The Proportion Saying COVID One Of The Biggest Issues
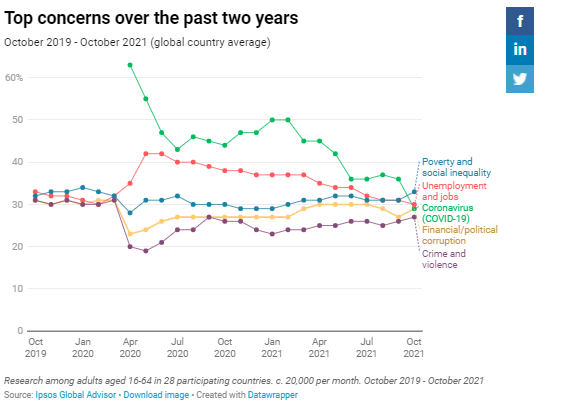
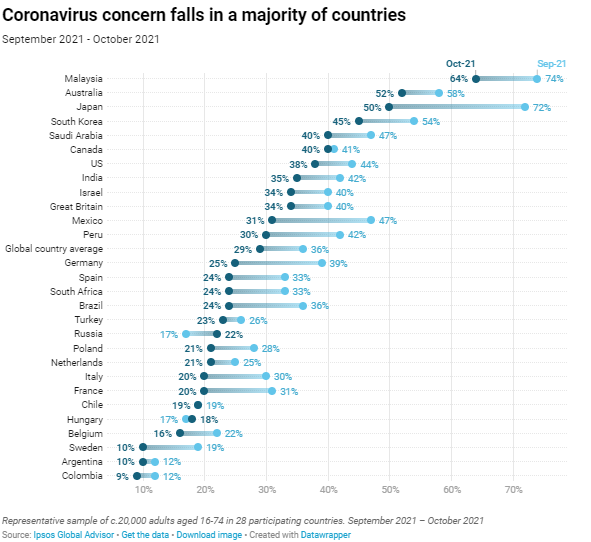
Facing Their Country Has Fallen From 36% To 29% (Global Country Average)
Since September Within 28 Countries Coronavirus falls from first to third place
in our monthly ranking of 18 issues. The proportion saying it one of the
biggest issues facing their country has fallen from 36% to 29% (global
country average) since September. All but three of the 28 countries surveyed
register declines in levels of concern about Coronavirus – most significantly
Japan (-22 points), Mexico (-16), Germany (-14), Peru (-12) and Brazil (also
-12). (Ipsos
MORI) 26
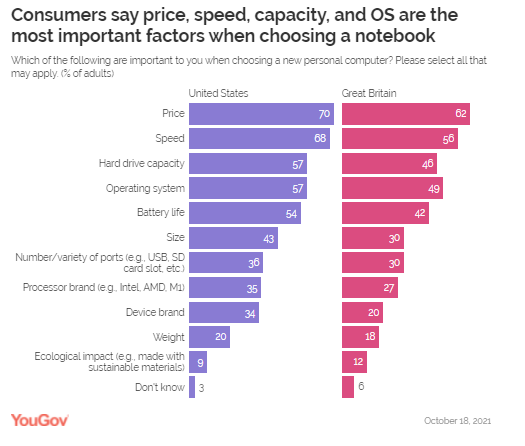
October 2021 Source: https://www.ipsos.com/ipsos-mori/en-uk/what-worries-world-october-2021 About A Third Of Consumers In The UK (35%) And About A
Quarter Of Those In The US (27%) Say The Processor Brand Is Important To
Them When Buying A Laptop About a third of consumers in the UK (35%)
and about a quarter of those in the US (27%) say the processor brand is
important to them when buying a laptop. Those figures are higher among those
who use laptops for creative work (39% in the US, 43% in the UK) or for
gaming (53% in the US, 52% in the UK). A plurality of consumers (43% and
39% in the UK) says 15 to 16 inches in the ideal size, while the 13- to
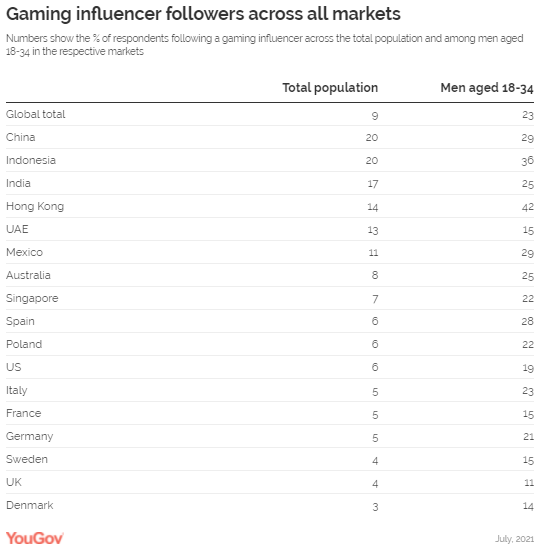
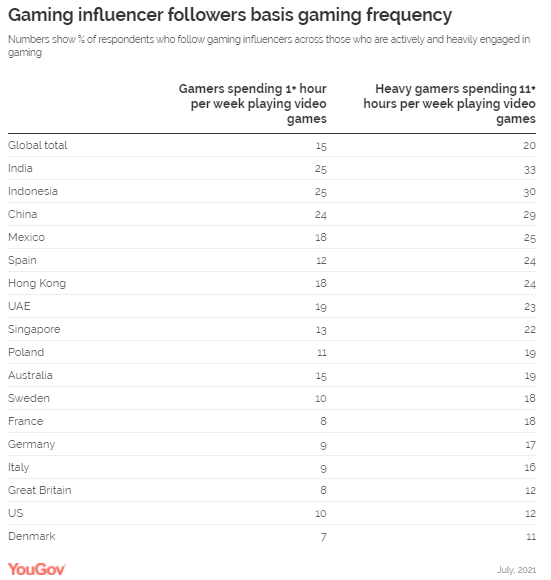
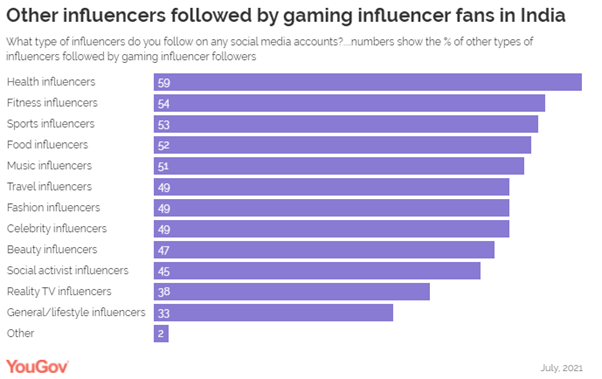
14-inch range is the next most popular (31% in the US, 35% in the UK). (YouGov UK) October 26, 2021 Young Urban Indian Males Are The Most Likely To Follow
Gaming Influencers, Survey Conducted In 17 Markets YouGov’s new gaming report shows that a
quarter of young urban Indian males between 18-34 years follow gaming
influencers in India. When it comes to the type of influencers followed among
adults of all ages, data suggests that just under one in ten (9%) consumers
across all 17 markets follow gaming influencers. However, this changes
significantly when we look at different demographic groups. Globally, gaming
influencers are the most popular type of influencer followed by males aged
18-34 years, with almost a quarter (23%) of all adults in this demographic
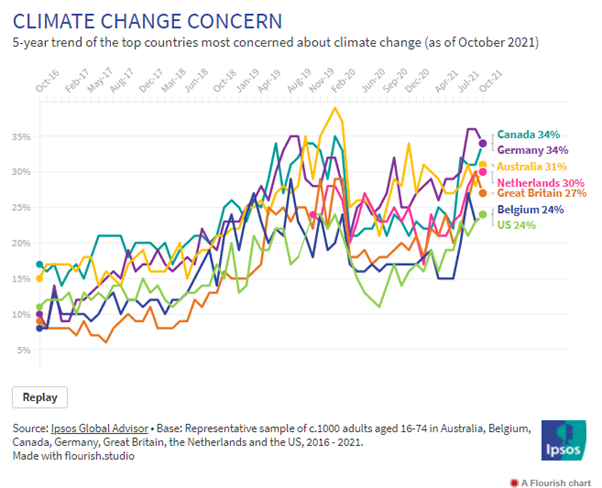
segment following gaming personalities. (YouGov India) Source: https://in.yougov.com/en-hi/news/2021/10/27/young-urban-indian-males-are-most-likely-follow-ga/ UK Public Highly Supportive Of COP26 Goals Among G20 Countries
But Few Expect The Government To Take The Steps Needed In a survey of 9,999 UK adults aged 16+,
three-quarters (76%) agree the UK should do more to combat climate change.
However, ahead of COP26, there is low confidence that the government will
deliver on climate, as over half (55%) are not confident that the government
will take the actions needed to help combat climate change within the next
few years (40% are confident). (Ipsos MORI) 28 October 2021 ASIA
714-43-01/Polls PM Modi’s
Approval Rating Among Urban Indians Has Improved Since August 2021 From 53%
To 58%
YouGov’s political tracker, that tracks
public opinion on politics and government affairs in the country shows PM
Modi’s approval rating among urban Indians has improved since August 2021,
when we first started tracking this data, from 53% in the beginning of August
(9th August 2021) to 58% in October (18th October). The improvement in his rating since August
corresponds to the waning impact of the second wave of Covid-19. However, it
peaks in early October, highlighting the positive impact of his recent US
visit on his perception among urban Indians. Approval for PM Modi is the highest among
residents of North India- at 63%. On the other hand, disapproval is the highest
among South Indians (at 36%). Public perception of the country’s
direction has also improved slightly during this period; from 53% saying
things in this country are headed in the right direction in early August to
59% saying this now (18th Oct). According to the public, unemployment,
women’s safety, and corruption are considered as the top three issues faced
by the country today. While unemployment is a bigger concern in East and
North East India (at 45%), women’s safety is believed to be a more dominant
issue in South India (at 37%). When looking at the perception of people
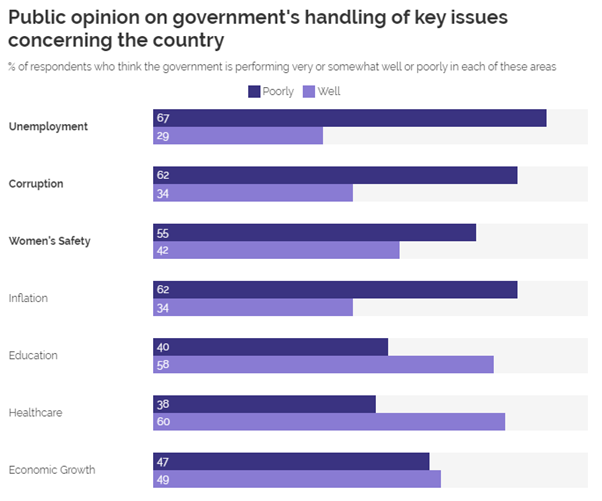
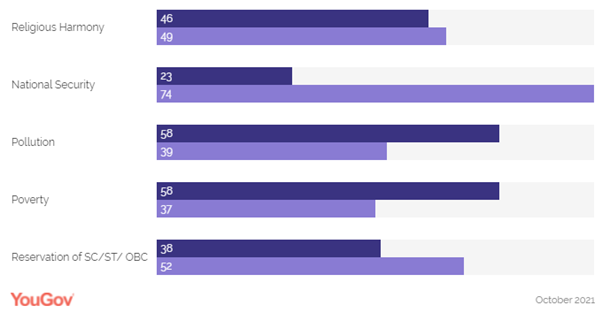
around the government’s performance in key concerning areas, we see that
two-thirds of urban Indians (67%) think the government is handling the issue
of unemployment very or somewhat poorly. Similarly, the proportions for those who
rate the government’s handling of the issues of corruption and women’s safety
poorly are 62% and 55%, respectively. However, public’ rating is more positive
than negative for issues such as national security, healthcare, education and
reservation of SC/ST/OBC, where people are more likely to say the government
is doing a good job in these areas. Even though a majority thinks the
government’s performance in key concerning areas is not satisfactory, they approve
of the way the Prime Minister is handling his job and generally think the
country is headed in the right direction. With Covid stabilising in many parts of the
country and the economy reopening to a great extent, there is hope for a
brighter future. YouGov will continue tracking the public sentiment around
government affairs to see how world events affect the opinion of people. (YouGov India) October 28, 2021 Source: https://in.yougov.com/en-hi/news/2021/10/28/how-has-pm-modis-approval-rating-changed-his-meeti/ MENA
714-43-02/Polls 86% Of The
Population Believe That Domestic Inefficiency And Corruption Have Had The
Worst Impact On The Iranian Economy’s Current State
The survey titled “Iranians’ Attitudes
toward International Relations” was conducted September 21-30, 2021. Around
23 thousandrespondents participated in the study. The final sample used in this
report consisted of 20,097 Iranians
living inside Iran. This study’s findings reflect the views of literate Iranian residents aged above 19 or
85% of Iran’s adult population. The results can be generalized to
the target population with a 95% credibility level and credibility intervals
of 5%. – According to this survey, 86% of the
population believe that “domestic inefficiency and corruption” have had the
worst impact on the Iranian economy’s current state. On the other hand, about
10% believe that “foreign sanctions and pressures” are the main cause of the
current state of Iran’s economy. – Over half of the population agree that
disputed matters in addition to the nuclear program should be negotiated with
the West to revive the JCPOA. About 42% of the population also think that the
JCPOA agreement benefitted the Iranian people before the USA withdrew from
it, while 37% disagree with this view. – 56% agree with Iran having a nuclear
program for exclusively peaceful purposes. About 11% agree with developing a
nuclear weapon, while 27% entirely oppose a nuclear program. – 55% agree with suspending uranium
enrichment to lift sanctions. About 27%, on the other hand, believe that Iran
should continue to enrich uranium, even if that entails the sanctions regime’s
continuation. – 37% said to agree with Iran’s
ballistic-missile development program if it does not lead to sanctions. On
the other hand, 26% agree with the missile program, even if sanctions are
imposed in response. About 28% entirely oppose the missile development plan. – Regarding other countries’ and
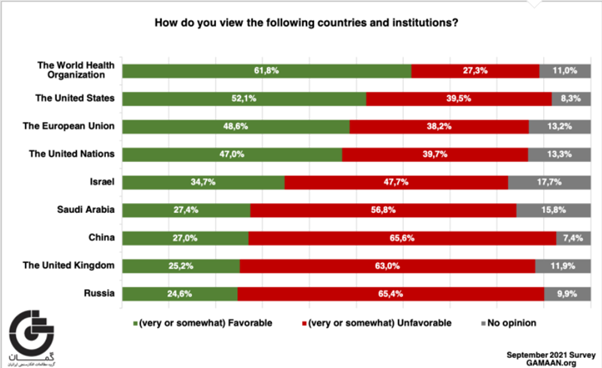
international institutions’ favorability, 52% said to have a positive view of
the USA while 39% have a negative view; 35% viewed Israel positively versus
48% negatively; 49% have a positive view of the EU and 38% have a negative
view; 25% have a positive view of Russia and 27% of China, while respectively
65% and 66% have a negative view; 27% have a positive view of Saudi Arabia
while 57% have a negative view; 25% expressed a positive view and 63% a negative
view of the United Kingdom; respectively 47% and 62% expressed a positive
view of the United Nations and the World Health Organization. – In response to the question, “Which USA
president’s foreign policy has most benefitted the Iranian people?”, only 7%
selected Joe Biden versus 29% who chose Donald Trump. 49% said neither
president’s foreign policy benefitted the Iranian people. – 47% consider the USA’s withdrawal from
Afghanistan to be detrimental to regional security, while 26% have the
opposite view. – 71% oppose the “Iran-China 25-year
Cooperation Program” and also 71% oppose the “agreement between Iran and
Russia regarding the legal regime of the Caspian Sea”, while 13% favor the
latter. 66% oppose the “20-year Cooperation Treaty between Iran and Russia”
and 15% support the agreement. – 61% believe that world powers should
monitor and, if necessary, take actions in response to the human rights
situation in Iran. About 15% believe that world powers should not interfere
in this matter, while 13% say that world powers should restrain themselves to
monitoring and reporting. – 57% evaluate Iran’s role in Syria in
recent years negatively and 26% evaluate it positively. About 34% believe
that the IRGC’s Quds Force’s regional activity has increased Iran’s security.
In contrast, 32% think these measures reduce Iran’s security, and 21% think
they have had no effect on Iran’s security. – 73% express their opposition to the
public chanting of “Death to America”, while 18% favor it. 65% oppose “Death
to Israel”, while 23% favor it. 64% agree with “Neither Gaza, nor Lebanon, I
sacrifice my life for Iran”, while 24% oppose it. 73% agree with “Our
enemy is right here, they lie that it’s the USA”, while
15% oppose it. – About 70% of the population oppose the
Islamic Republic of Iran’s approach to Hezbollah in Lebanon, Hamas in
Palestine, Al-Hashd al-Shaabi in Iraq, the Houthis in Yemen, and Bashar
al-Assad’s regime in Syria, while about 21% agree with Iran’s approach to
these groups. – Regarding the tension between the Islamic
Republic of Iran and Israel, about 53% consider the probability of a direct
military conflict between the two countries to be low, while 32% believe that
the possibility of a direct military conflict is high. – The results of this poll show that about
32% participated in the June 2021 presidential election and that 23% of the
eligible voters chose Ebrahim Raisi. Also, about 5% of eligible voters cast
blank ballots. – Regarding Iranians’ political
orientation, 35% want the overthrow of the Islamic Republic, 24% prefer
structural changes and a transition from the Islamic Republic, while 16% want
to preserve the principles and values of the revolution, and
12% seek reforms within the Islamic Republic. 13% selected none of these
options. (Gamaan) October 27, 2021 Source: https://gamaan.org/2021/10/27/ir-survey-english/ AFRICA
714-43-03/Polls A Majority
(55%) Of Sudanese “Disapprove” Or “Strongly Disapprove” Of Military Rule
A majority of Sudanese reject military rule
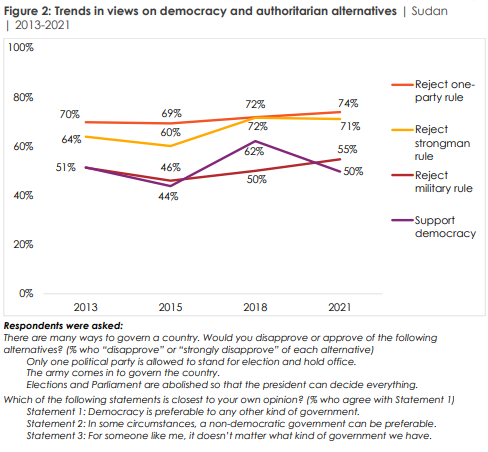
and other non-democratic regimes, the most recent Afrobarometer survey shows. Findings from a national survey in early
2021 show that public opposition to military, strongman, and one-party rule has increased
since 2015. Although only half of citizens declare a
preference for democracy over any other political system, democracy supporters outnumber
those who think non-democratic systems can be preferable by about 2-to-1. Sudan’s transition to democracy has been
led by a hybrid military-civilian government since a popular uprising forced President Omar
al-Bashir from office in 2019. But after an unsuccessful coup attempt in September,
Prime Minister Abdalla Hamdok and other ministers have been arrested in an apparent coup
Monday morning. Key findings ▪ A majority (55%) of Sudanese
“disapprove” or “strongly disapprove” of military rule. Even larger majorities reject one-party
rule (74%) and presidential dictatorship (71%) (Figure 1).
▪ Half (50%) of citizens prefer
democracy to any other form of government – almost twice as many as think that non-democratic
systems of governance can be preferable in some circumstances (28%). ▪ Opposition to rule by the military
has increased by 9 percentage points since 2015. Disapproval of being governed by an
autocratic president or by a single political party has also increased (by 11 and 5
points, respectively). (Afrobarometer) 25 October 2021 714-43-04/Polls Unemployment
Is The Problem Mostly Widely Seen As A Top Priority For Government Action,
Cited By Six In 10 South Africans
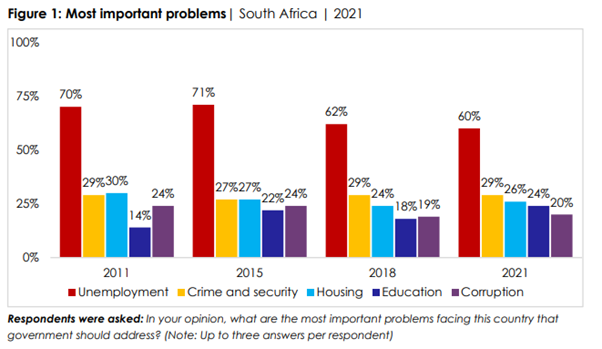
Continuing a decade-long demand, South
Africans rank unemployment as the country’s most important problem that the government
urgently needs to address, the latest Afrobarometer survey shows. A lack of jobs continues to outrank crime,
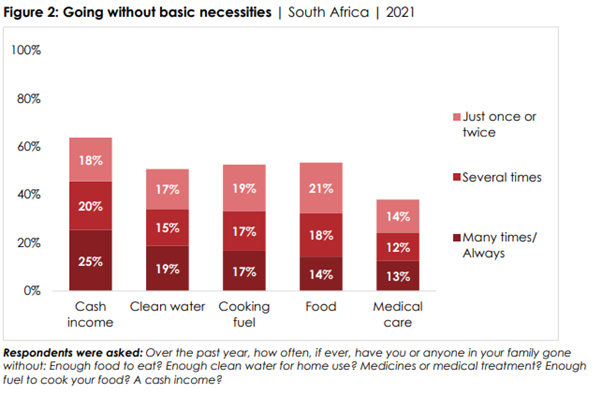
housing, education, and corruption among citizens’ priorities for government action. Indeed, a majority of citizens report going
without a cash income at least once during the year preceding the survey. Many also experienced
shortages of other basic necessities such as clean water, food, medical care, and cooking
fuel. Citizens indicate that they would be
willing to pay more taxes to support programs to help young people, the demographic bearing the brunt
of the jobs crisis. They say that if the government decided to increase its spending on such
programs, job creation should be the highest priority for additional investment. Key findings ▪ Unemployment is the problem mostly
widely seen as a top priority for government action, cited by six in 10 respondents (60%). Job
creation has been at the top of the list for the past decade (Figure 1). ▪ Almost two-thirds (63%) of South
Africans say they went without a cash income at least once during the year preceding the survey,
including 25% who did so “many times” or “always.” Many also experienced frequent
shortages of food (14%), clean water (19%), medical care (13%), and cooking fuel (17%)
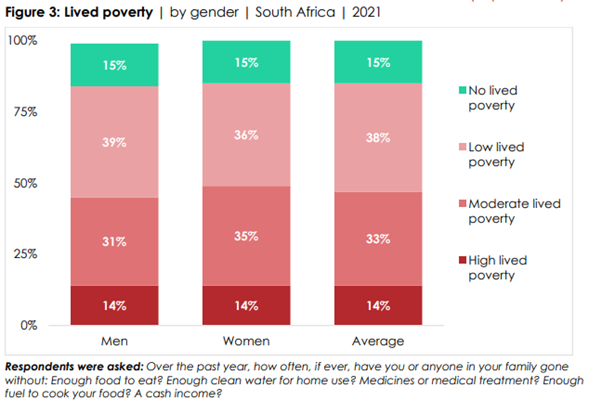
(Figure 2). ▪ Based on these reported shortages,
almost half (47%) of South Africans experienced either high (14%) or moderate (33%) lived poverty
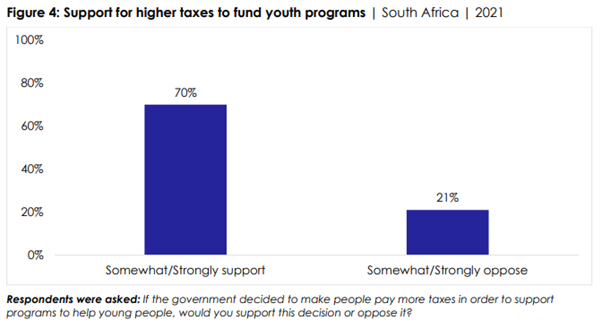
(Figure 3). ▪ Seven in 10 (70%) citizens say they
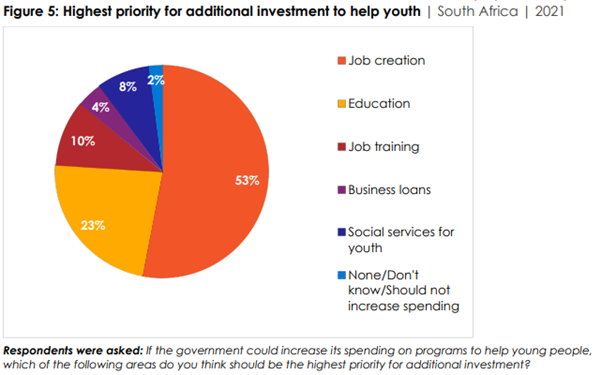
would be willing to pay higher taxes to fund youth programs (Figure 4). ▪ More than (53%) say that if the
government could increase its spending on programs to help young people, the highest priority for
additional investment should be job creation (Figure 5). (Afrobarometer) 26 October
2021 714-43-05/Polls Only About A
Quarter (24%) South Africans Are Very Satisfied With The Party They Voted For
In The 2016 Local Government Election
Research
recently undertaken by Ipsos, on behalf of the eNCA, revealed these and other interesting
findings about the South African electorate and prevailing opinions on local
government. The study was undertaken between 9 and 14 October 2021 and made
use of a CATI methodology (Computer Assisted Telephone Interviewing). Does your local authority work for you? Clearly,
many of the current local authorities do not work optimally or not at all for
South African voters, as almost half (47%) of those who are registered to
vote on 1 November 2021, say they are very or somewhat dissatisfied with the
party they voted for in the 2016
local government election. As can be
seen in the graph below, only about a quarter (24%) is very satisfied with
the party they voted for in the 2016 local government election and a further
quarter (26%) is somewhat satisfied.
Looking into
these results more closely, we see that women are a little bit more forgiving
than men, with 44% of women indicating that they are somewhat or very
dissatisfied in their 2016 choice, while half (50%) of men is dissatisfied.
It is also clear that current registered voters between the ages of 25 to 54
are the most dissatisfied, while those who are a little bit older or younger
are slightly more forgiving:
Do you know your ward councilor? This feeling
of dissatisfaction may have something to do with the fact that few registered
voters have met their ward
councilor candidate:
While the
function of local government is to be the “coalface” where voters can
interact with their political representatives, and can easily contact their
councilors and expect some action or answers about issues in the local area,
it seems that candidates for the position of councilor are rather “voter
shy”. Only a third
(33%) of registered voters have met and/or know their candidates, while 34%
have never met him or her. There is a further third (33%) who say that they
vote for a political party and not specifically for the ward councilor.
However, in our election system of proportional representation, the
opportunities for direct interaction with a candidate is low, we can thus
possibly assume that these people also have no idea about who their
candidates are – or what they promise to do. In addition,
the larger political parties use their high-profile leaders in the campaigns,
which are mainly driven on a national stage, with the launches of national
manifesto’s, rallies, and meetings (sometimes within the Covid-19
regulations). Therefore, the campaigns at a local level, if they exist, are
rather watered down. As a result of this the real local issues do not get
much attention in campaigns, and national issues dominate and drive the
discourse, like the vaccination drive to halt Covid-19 infections or
unemployment and job creation – things that can only partly be addressed by
local authorities. Voters want local governments to focus on safety and security Another
example of such a national issue overflowing into the area of local politics
is that of safety and security. This can be seen in a recent poll that Ipsos
undertook in 26 countries, giving respondents a list of people in different
professions and then asking: “In general, do you think each is trustworthy or untrustworthy in
your country? From the
table below it is clear that only 13% expressed trust in the police – the
lowest proportion of all 26 countries.
In the eNCA pre-election study, Ipsos asked
registered voters to indicate: “Which one of the following basic services is the most important when
you decide who to vote for in the Local Government Elections?” The three
choices offered were:
In view of
the results of the previously shared international results, it should
probably be no surprise that registered voters chose “Safety and Security”
above the two other options by wide margins.
“Safety and
security” were also mentioned as a top priority by the registered voters in
all provinces. The agenda of local governments is thus rather clear in terms
of what should be addressed in the coming months – together with the list of
other things mentioned by voters.
What are the best and the worst things about the area where you live? Feelings
about the area where voters live were probed by two deceptively simple questions:
We have
already seen that safety and security are priorities for registered voters,
what else would they like the local authorities to sort out?
The two
worst things chosen were that facilities for young people were inadequate in
the area and that municipal councilors were incompetent / corrupt or did not
do their jobs. In the case
of young people and things for them to do, we do believe that respondents
looked at this holistically and meant opportunities to find work,
opportunities to study, opportunities to use their skills and entertainment
facilities. In view of
the large number of municipalities currently under administration or in
financial distress and the report delivered in early 2021 to Parliament that
47% of senior municipal officers do not have the minimum competency level to
do their jobs, the only way that incompetent or corrupt candidates can be
weeded out is if they are not receiving enough votes in this election. This
is largely up to the electorate next Monday.
Although
almost a fifth (17%) see nothing good in the area where they live, a similar
proportion (18%) are happy with their choice of residence and around one in
every ten (9%) think that they live in a beautiful area. There is also good
access to amenities in some areas and 9% say that their ward councilor does
care about the area. However, to
underline many of these findings, only 5% think that they have a competent
local authority. (Ipsos South
Africa) 26 October
2021 Source: https://www.ipsos.com/en-za/local-authorities-do-not-live-expectations-voters 714-43-06/Polls In Recent
Pre-Election Surveys Support For The ANC Has Been Measured Consistently Below
50%
In recent pre-election surveys support for
the ANC has been measured consistently below 50% - a phenomenon not seen
commonly before. This is the most interesting finding in
the eNCA/Ipsos pre-election series of opinion
surveys. Three waves of this study were conducted during October 2021. Since
the 1994 elections, results of both national and local government elections
have always returned the ANC with countrywide support well above
50%. A quarter (25.5%) of registered voters did
not choose a party to vote for in wave 1. In wave 3, almost a third (31%) did
not choose a party to vote for. A wide variety of explanations were given:
some people indicated that they will not vote in the local government
elections, while others expressed distrust of politicians and political
parties. Some respondents were of the opinion that voting won’t change
anything, and others just refused to answer the question. These findings reiterate a comment
expressed in an earlier press release on the eNCA/Ipsos project, namely that
voter apathy can be an important variable in this election (A
third of South Africans will decide the outcome of the local government
elections). Over the last number of years news reports
did point out the internal strife of different factions in the ANC, and also
reported on corruption issues and financial difficulties experienced by the
party. It is interesting that opposition parties did not benefit in terms of
support during the previous few years of difficulty for the ANC – but then,
the news items on factional issues, corruption and financial difficulties
were not limited to the ANC and many other parties and political leaders were
also reported on. The period since the 2019 national and provincial
elections was not easy for any political party in South Africa. Add to this
the Covid-19 epidemic, the slow pace of vaccinations, the issues of service
delivery and governance in the majority of municipalities, loadshedding and
water supply issues and the current rushed and shrunken election campaign, it
is impossible to predict with certainty the outcome of these rather messy and
unique elections.
The total number of South Africans
registered to vote are just over 26,2 million – and it is clear that all
registered voters will not turn out to vote on 1 November 2021. If we just
look at the group who indicated that they want to vote, the ANC support will
be 43.4%, that of the DA 24.2% and the EFF support will stand at 14.8% Looking at answers given to different
questions, a model was developed to identify three possible scenario’s – a
high, medium and low voter turnout scenario. This model was refined
over the three waves of the eNCA/Ipsos pre-election polls.
Looking at the outcomes of the model, the
most probable outcome will be between the medium and the high voter turnout
scenarios. The performance of political parties is influenced fundamentally
by different turnout outcomes. For instance, a low turnout scenario will be
to the benefit of the DA, and the detriment of the ANC. The model is not
linear and different scenario’s influence different parties differently.
(Ipsos South Africa) 31 October 2021 Source: https://www.ipsos.com/en-za/ruling-party-shedding-support WEST
EUROPE
714-43-07/Polls Britons Are Most Likely To Expect Big Delays In Parcel Deliveries For
Online Shopping (58%)
With Britain still in the grip of the supply chain crisis, the media
have been reporting industry concerns that certain products will be in short
supply for Christmas this year. Additionally, with COVID cases remaining stubbornly high, talk has
turned to the necessity of reintroducing restrictions during the festive
period. How plausible do Britons consider these warnings? And how much would
it actually matter to people if they weren’t able to fulfil some Christmas
traditions this year? Gift-giving Britons are most likely to expect big delays in parcel deliveries for
online shopping (58%). This includes 17% who consider it “very likely”. That
being said, fewer Britons think it will actually be harder to find Christmas
presents this year (37%). Being unable to give loved ones presents this year is one of the most
upsetting prospects to Britons, with 60% of people saying they would find
this distressing. People are far less bothered by the potential that they
themselves would not receive any gifts as a result of supply shortages, at
just 27%. This means that the prospect of present delays and being unable to
give people presents is the most upsetting scenario that Britons consider
most likely to happen.
Seeing loved-ones The most upsetting thing that could happen at Christmas this year is
being unable to see close family. Three quarters (74%) of Britons say this
would rile them, including 45% who would be “very upset”. Most Brits would
also be upset about not being able to see friends (54%), as would 44% at the
prospect of not seeing extended family. Far fewer people see this as a realistic prospect than parcel
shortages, however. In their role as Ghosts of Christmas Yet to Come, only
one in three Britons (32%) see it as likely that new restrictions will be put
in place preventing people from mixing with those from outside their
household. A lower number (17%) go further still, expecting a festive return
to full national lockdown, including restrictions on leaving the home. Food Many Britons also expect shortages
of turkey this year (49%), following stories in the press. However,
few Britons would actually be bothered by the lack of a gobbler on the table
(18%). Four in ten people (40%) think there will be shortages
of pigs in blankets, with 19% saying they’d be upset if they couldn’t
have the double-pork treats. Previous YouGov research has
shown that roast potatoes are the most important component of a Christmas
dinner, and the data bears this out. While far fewer Britons expect shortages
of potatoes (20%), almost half the population (47%) would be
distraught if they couldn’t have tubers for their festive feast. Grazing around mealtimes could also be affected, with reports
emerging that Quality
Street could be in short supply. One in five Britons suspect there will
be shortages of chocolate selection boxes (22%), while a similar proportion
would be upset if this came to pass (20%). Demographics Across the board, younger Britons are more likely to be upset by the
potential Christmas restrictions and shortages than their older counterparts.
The only exceptions are for seeing close and extended family, where levels of
distress are largely consistent across the generations. Because a person’s vote is so heavily connected to their age, this
does mean that Labour voters are more likely to be upset about potential
shortages than Tories. However, the gap here is narrower than between
generations alone. Labour voters are, however, substantially more likely than
Conservative voters in many cases to expect Christmas shortages. (YouGov UK) October 28, 2021 714-43-08/Polls Three-Quarters Of Britons Expect Halloween To Go Ahead As Normal This
Year
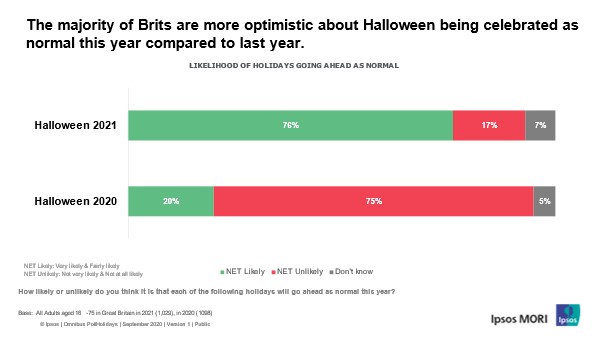
New research by Ipsos MORI shows high hopes for Halloween fans in
2021 as 76% of Britons expect Halloween to be celebrated as it normally would
this year. This time last year, only 20% thought it was likely to continue as
usual. A similar proportion (77%) expect households to mix freely.
All Halloween activities look set to go ahead, 10% say they
will take a child trick-or-treating this year (10% say they normally do this)
while 11% will visit friends/family in another household (10% normally) and
6% will go to a pub/restaurant (6% normally). Slightly fewer will host
Halloween festivities, 11% say they normally would have friend/family from
outside of their household visit their home, only 7% expect to do so this
year. While many don’t celebrate Halloween, a third (34%) are looking
forward to it a great deal or a fair amount with 14% saying they will enjoy
it more this year than normal. Keiran Pedley, Research Director at Ipsos
MORI, said: The British public are much more optimistic
about Halloween going ahead as normal this year than they were last year.
Although pessimistic about the direction of the country generally, they are
clearly more confident that life is returning to some semblance of normality
in terms of household mixing and the celebration of holidays. (Ipsos MORI) 29 October 2021 Source: https://www.ipsos.com/ipsos-mori/en-uk/three-quarters-britons-expect-halloween-go-ahead-normal-year 714-43-09/Polls At Least One In Five Women Haven’t Checked For Signs Of Breast Cancer
In The Last Year
October marks breast cancer awareness month. Despite being the most
common cancer in the UK there is a misconception among some that it only
affects women. A new YouGov survey asks both British men and women when, if
ever, was the last time they did a self-check, and if the disease has
impacted their lives. While screening for breast cancer is routine for older women, the NHS
recommends that all women are ‘breast
aware’ so they can spot the signs and symptoms of the disease.
Breast cancer awareness charity CoppaFeel recommends self-checks for signs of
the disease should be a monthly habit for
both men and women. Among women, three quarters (76%) say they have ever checked
themselves for signs of breast cancer. This includes two in five (41%) who
say they have done within the last month, and 18% say they have done so in
the last six months. Just 11% of women say they’ve never done so. While eight in ten men (80%) are aware that they too can
develop breast cancer, only 19% of men say they have ever done a breast
exam themselves. This includes some 6% who say they have done one in the last
month. Approaching seven in ten (69%) say they have never performed a
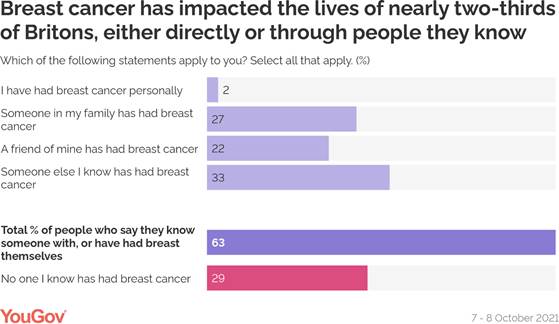
self-check for signs of breast cancer. Breast cancer has affected the majority of
Britons in some way While cancer will affect around one in eight women directly
in their lifetimes, a diagnosis can affect an entire family. Overall, nearly
two-thirds of Britons (63%) say the disease has been part of lives. A quarter (27%) of people have a family member who has had breast
cancer, 22% have had a friend diagnosed with the disease and 2% say they have
had it themselves. Another 33% of people have a different acquaintance who
has had breast cancer. Only 29% don’t know anyone who has had breast
cancer.
Among older Britons, the proportion of those saying they know someone
who has had breast cancer rises to three in four (75%). Women are also more
likely to know or have known someone with the illness (72%) compared to men
(53%). (YouGov UK) October 29, 2021 714-43-10/Polls 51% Of The Public Say They Would Be Personally Unwilling To Stop
Flying For Leisure
With COP-26 fast approaching, the government have announced that
subsidies to replace old boilers will be available from next year with a plan
to no longer allow the sale of new gas boilers by 2035. This follows a
previously announced policy of banning the sale of all petrol and diesel cars
by 2030 as the UK strives for net-zero emissions. As action to tackle climate
change ramps up, YouGov has tested support and perceived effectiveness of
several potential policies, ranging from those already in the pipeline to
more draconian restrictions. The key finding from these results is that support and effectiveness
correlate very strongly, with policies that are seen as being effective also
being highly supported, and those that are seen as being less effective
receiving little support. On the face of it, this suggests that increasing how effective the
public view a measure will increase support. However, it could actually be
the other way round: there is some evidence in the results that the public
may be rejected the effectiveness of some of the more extreme measures we
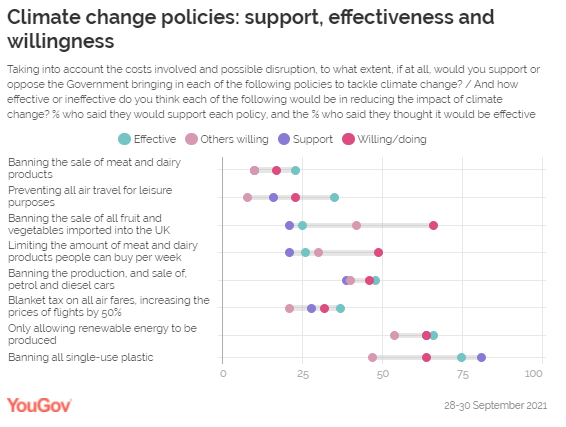
tested due to viewing them unfavourably or as impractical. For example, 46% thought introducing a ‘frequent flyer levy’ would be
an effective measure, while only 35% thought preventing all air travel for
leisure an effective measure. Clearly, banning large numbers of flights would
cut more emissions than anything that could be done with the money raised
from a levy of the small number of people who fly frequently. While it may be
that the public view the first measure as a more impactful way to reduce CO2 emissions,
it is more likely the difference here is down to objection towards the policy
(75% oppose a leisure air travel ban, compared to only 25% for a frequent
flyer levy). Indeed, 51% of the public say they would be personally unwilling to
stop flying for leisure, compared to 23% who are willing to do so or already
doing so. Further, 76% believe most other people would be unwilling to make
this change. This suggests that perceived effectiveness may also be being
driven by its personal lifestyle impact and/or that the policy would be
rejected by the public, rather than just its potential impact on climate
change. Another area where perceived effectiveness is at odds with what
emissions levels would suggest could make a big impact is changes to diet.
Again, we see that the less publicly palatable option is seen as less
effective, even where logic would dictate it should be more effective: while
support for limiting meat and dairy consumption is supported by twice as many
as banning it altogether (21% to 10%), the latter is seen as slightly less
effective (23%) than the former (26%). Comparing these results with personal willingness actually tells a
different story to the air travel results. Far more Britons claim to be
personally willing to partially cut down meat and dairy in their diet (49%)
than the levels of support for the policy might suggest, and are slightly more
likely to cut them out completely (17%). Perceived unwillingness on the part
of others, however, tracks more closely with support and effectiveness
levels. Just three in ten (30%) think most people would be willing to cut
back on meat and dairy, and only 10% say the same of cutting it out entirely. This could indicate that higher levels of personal willingness are
based on an acknowledgement of the need to change their diet (whether this be
for environmental or other reasons such as health), but that ultimately the
policy is being rejected on the grounds that it’s too much of an overreach
for the state to control people’s diets so strictly. Looking at the five most supported policy ideas from the 21 we
tested, there is again a strong correlation between the two measures, but
support outranks perceived effectiveness in each one. Planting more trees or
introducing government subsidies to make homes energy-efficient are overtly
positive actions when asked in isolation, so it is not too surprising that they
are strongly supported. What is trickier to judge here is whether perceived
effectiveness in tackling climate change is boosting support, or vice-versa.
It could be that the public see these as “easy wins” with minimal personal
impact and therefore an effective way to tackle the problem. The two policy areas where support outranks effectiveness the most
are banning cryptocurrency (45% support, 26% effective) and the
aforementioned ‘frequent flyer levy’ (60% support, 46% effective). Both
policies would impact a relatively small proportion of the population as very
few Brits invest in cryptocurrency or fly regularly, so this lack of skin in
the game may allow a greater number of people to feel able to support them.* (YouGov UK) October 31, 2021 714-43-11/Polls 73% Of Employers In France
Suffer From Poorly Mastered Written And Oral Expression By Their
Teams, All The More So In A Period Of Widespread Teleworking
Among the main lessons of the study
As long-distance exchanges multiply and informal moments of
communication become rarer, expression and spelling skills are essential:
precision, disambiguation, conciseness are invaluable in avoiding
misunderstandings.
In the recruitment process, fluency in French is more important than
fluency in English This statement sounds like a no-brainer. However, over the years
of globalization, a good level of English has been an undeniable advantage in
hiring. At a time when the internationalization of trade has come to a
halt, the employment passport has changed scope, and mastery of expression
and spelling has become a priority.
French language certification makes the
difference with employers Aware of these growing challenges, companies, higher education
establishments and schools encourage their employees, students or pupils to
improve the quality of their expression. To motivate them, display their
progress, certify their level, these players resort to certification in
French, a possibility still little known to the general public. A lever
for employability?
(Ipsos France) October 26, 2021 714-43-12/Polls 2022 Fifa World Cup: 62% Of French People Think The France Team Will
Win In Qatar
The second edition of the Nations Football League ended in style with
the success of the Blues in the final against Spain, a few months after its
premature exit in the knockout stages of Euro 2020. If the flash study * led
by Ipsos shows that this competition remains relatively unknown, it has in
any case boosted the morale of the supporters, who are more than 6 out of 10
to see a victory in Qatar next year. The League of Nations, a competition still
relatively confidential If the victory of the French will undoubtedly convince football
enthusiasts to watch the next League of Nations, the study carried out by
Ipsos testifies to a need to anchor this meeting - of which it was only the
second edition - in the minds of the French and football fans. “The competition must indeed find its place between the Euro and the
World Cup, because only 44% of aficionados agree to see in the League of
Nations a prestigious competition today. A finding that is improving
nonetheless among 16-24 year olds (57%). », Comments Damien Barnier, MSU
Research Director at Ipsos in France. However, nearly two-thirds of football enthusiasts (64%) find the
Nations League more interesting than classic friendlies: 27% strongly agree
with this opinion, 37% tend to agree. The world event every two years, an idea
that is difficult to convince But the League of Nations is not the only international competition
to have made the headlines lately. Indeed, the debate on the
organization of the FIFA World Cup every two years was recently launched by
Arsène Wenger, director of world football development at FIFA. A
possibility which, for the time being, struggles to convince football fans. Thus, 46% of football fans reject the idea of a
biennial World Cup rather than every 4 years: 29% do not agree at all with
this idea, 17% tend to disagree. On the other hand, only 25% of football
followers agree with this project launched by the former Arsenal
coach. It is however interesting to note that 16-24 year olds are more
likely to subscribe to this idea: 48%, against only 19% rejecting it. One year before the World Cup, optimistic
supporters After its victory in the League of Nations, is France a favorite to
win in Qatar in just over a year? For 52% of French football followers,
the recent victory of the Blues in the Nations League is significant for the
2022 World Cup.
(Ipsos France) October 27, 2021 NORTH
AMERICA
714-43-13/Polls 37% Of American Adults Say Spending On Police Should Stay About The
Same
Amid mounting public concern about violent crime in the United
States, Americans’ attitudes about police funding in their own community have
shifted significantly. The share of adults who say spending on policing in their area should
be increased now stands at 47%, up from 31% in June 2020. That includes 21%
who say funding for their local police should be increased a lot, up from 11% who said this last
summer. Support for reducing spending on police has fallen significantly: 15%
of adults now say spending should be decreased, down from 25% in 2020. And
only 6% now advocate decreasing spending a lot, down from 12% who said this last year. At the same
time, 37% of adults now say spending on police should stay about the same,
down from 42% in 2020. How we did this Views on police funding continue
to differ widely by race and ethnicity, age and political party.
White (49%) and Hispanic (46%) adults are more likely than Black (38%) or
Asian (37%) adults to say spending on police in their area should be
increased. Black adults (23%) are more likely to say that police funding
should be decreased than those who are White (13%) or Hispanic (16%). Some
22% of Asian adults say spending should be reduced, which is statistically
higher than the share among White adults but not higher than the share among
Hispanic adults. Majorities among those ages 50 and older favor increased spending on
police, including 63% of those 65 and older. Young adults remain the biggest
proponents of decreased police funding: Roughly a third (32%) of those ages
18 to 29 say there should be less spending on police in their area. This
compares with 18% of those ages 30 to 49 and fewer than one-in-ten of those
50 and older. Partisanship is strongly linked with views of police funding. A
majority of Republicans and independents who lean to the Republican Party
(61%) say spending on police should be increased, with 29% saying it should
be increased a lot; 5% of Republicans say spending should be decreased, and
33% say it should stay about the same. By contrast, 34% of Democrats and Democratic leaners say police
funding should be increased, 25% say it should be decreased and 40% would
like to see it stay about the same. Since 2020, the views of Black Americans and Democrats have changed
more than the views of White and Hispanic adults and Republicans when it
comes to decreasing funding for local police. The share of Black adults who
say police spending in their area should be decreased has fallen 19
percentage points since last year (from 42% to 23%), including a 13-point
decline in the share who say funding should be decreased a lot (from 22% to 9%). The share
of White and Hispanic adults who say funding for local police should be
decreased also declined over this period, but not as much. Similarly, the share of Democrats who say funding for local police
should be decreased has fallen markedly – from 41% in 2020 to 25% today. By
comparison, the share of Republicans who prefer less spending – which was
already quite low – has moved incrementally lower. Growing shares of
Republicans and Democrats alike now say police funding should be increased in
their area. Among Democrats, Black (38%) and Hispanic (39%) adults are more
likely than White adults (32%) to say spending on police in their area should
be increased. There is no significant difference across these racial and
ethnic groups in the share of adults who say spending should be decreased. Within the GOP, White and Hispanic adults differ in their views on
this question: 64% of White Republicans say police spending in their area
should be increased, compared with 53% of Hispanic Republicans. Relatively
small shares in each group – 4% of White Republicans and 9% of Hispanic
Republicans – would like to see spending go down. (There were too few Black
Republicans in the sample to break out separately.) The age gap in views about police funding has widened since 2020,
mainly because views have shifted more dramatically among those ages 50 and
older. The share of adults in this age group who say police spending should
be increased has jumped 22 percentage points since 2020 (from 37% to 59%),
while the increase has been more modest among those younger than 50 (from 26%
to 36%). Both age groups have seen a drop-off in support for reduced spending
on local police. These age patterns are similar among White and Black adults,
as well as across parties. Americans’ changing attitudes about police spending in their area
have occurred amid rising public concern about violent crime. In July 2021,
61% of adults said violent crime was a very big problem in the country today,
up from 48% in April 2021 and 41% in June 2020 (though concern over crime has
fluctuated in recent years). In the July survey, Americans expressed more
concern about violent crime than they did about the federal budget deficit
(50% said this was a very big problem), climate change (47%), racism (45%),
economic inequality (44%) and illegal immigration (43%). (PEW) OCTOBER 26, 2021 714-43-14/Polls Roughly One-In-Five Say That The Federal Government Should Stop
Enforcing The Separation Of Church And State (19%)
The First Amendment to the United States Constitution states that the
country shall have no official religion. At the same time, Christians continue
to make up a
large majority of U.S. adults – despite some rapid
decline in recent years – and historians, politicians and religious
leaders continue to debate the role of religion in the founders’
vision and of Christianity in the nation’s identity. Some Americans clearly long for a more avowedly religious and
explicitly Christian country, according to a March 2021 Pew Research Center
survey. For instance, three-in-ten say public school teachers should be
allowed to lead students in Christian prayers, a practice that the Supreme
Court has ruled unconstitutional. Roughly one-in-five say that the federal
government should stop enforcing the separation of church and state (19%) and
that the U.S. Constitution was inspired by God (18%). And 15% go as far as to
say the federal government should declare the U.S. a Christian nation. On the other hand, however, the clear majority of Americans do not
accept these views. For example, two-thirds of U.S. adults (67%) say the
Constitution was written by humans and reflects their vision, not necessarily
God’s vision. And a similar share (69%) says the government should never
declare any official religion. (Respondents were offered the opportunity to
reply “neither/no opinion” in response to each question, and substantial
shares chose this option or declined to answer in response to all of these
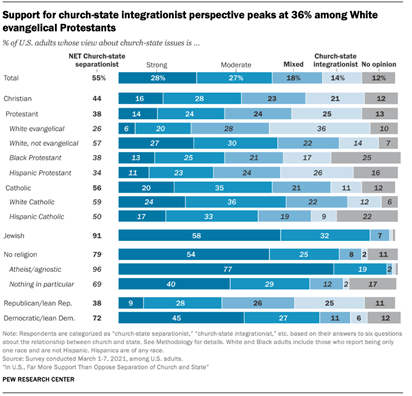
questions, suggesting some ambivalence among a segment of the population.) Perhaps not surprisingly, the survey finds that Christians are much
more likely than Jewish or religiously unaffiliated Americans to express
support for the integration of church and state, with White evangelical
Protestants foremost among Christian subgroups in this area. In addition,
Christians who are highly religious are especially likely to say, for
example, that the Constitution was inspired by God. But even among White
evangelical Protestants and highly religious Christians, fewer than half say
the U.S. should abandon its adherence to the separation of church and state
(34% and 31%, respectively) or declare the country a Christian nation (35%
and 29%). Politics also is a major factor. Republicans and those who lean
toward the Republican Party are far more likely than Democrats and Democratic
leaners to want to secure an official place for Christianity in the national
identity. However, for the most part, Republicans do not directly voice a
preference for the integration of church and state. For instance, 58% of
Republicans and Republican leaners say the federal government should never
declare any religion as the official religion of the United States, while a
quarter of Republicans (26%) say that the government should declare the U.S.
a Christian nation. By comparison, among Democrats and those who lean toward
the Democratic Party, 80% say the government should never declare any
official religion, and just 6% want the government to declare the U.S. a
Christian nation. While the above-average level of support for an overtly Christian
government among Republicans and White evangelical Protestants may come as no
surprise to close observers of American politics, some of the other patterns
in the survey are perhaps more unexpected. For example, many Black and Hispanic
Americans – groups that are heavily Democratic – are highly religious
Christians, and on several of the questions in the survey, they are just as
likely as White Americans, if not more likely, to say they see a special link
between Christianity and America. Nearly four-in-ten Black Americans (38%) say public school teachers
should be allowed to lead students in Christian prayers, somewhat higher than
the 31% of White Americans who say this. And about one-in-five U.S. Hispanics
(22%) say the federal government should stop enforcing the separation of
church and state, roughly on par with the 19% of White Americans who say
this. These are among the key findings of a Pew Research Center survey
conducted March 1-7, 2021, among 12,055 U.S. adults on the Center’s online,
nationally representative American Trends Panel (ATP). These questions about
the relationship between church and state can be combined into a scale that
sorts respondents into one of four categories – “Church-state
integrationists” (who say they would favor the intermingling of religion with
government and public life); “church-state separationists” (who favor a wall
of separation between religion and state); those who express “mixed” views
about these matters; and those who largely express no opinion. When the
questions are scaled together this way, they show there is far more support
for church-state separation than for church-state integration in the U.S.
public at large. How categories on church-state separation
scale were defined First, all respondents who said “neither/no opinion” or refused to
answer in response to four or more of the six items are placed in the “no
opinion” category. Next, all remaining respondents are sorted into one of three
categories – “church-state integrationists,” “church-state separationists,”
and “mixed.” Those who offered four or more church-state integrationist
answers (e.g., “Cities and towns in the U.S. should be allowed to place
religious symbols on public property” or “The federal government should stop enforcing
separation of church and state”) are placed in the “church-state
integrationists” category. Those who offered three church-state
integrationist answers also are placed in this category if they offered only
one or zero church-state separationist answers. Those who offered four or more church-state separationist answers
(e.g., “Cities and towns in the U.S. should keep religious symbols off public
property” or “The federal government should enforce separation of church and
state”) are placed in the “church-state separationist” category. Those who
offered three church-state separationist answers also are placed in this
category if they offered only one or zero church-state integrationist
answers. Respondents who offered three of one kind of answer and at least two
of the other kind are placed in the “mixed” category, as are those who
offered two of one kind of answer and two or one of the other kind of answer. Finally, because it is so large, the “church-state separationist”
category is sometimes divided into two groups in this report. “Strong”
church-state separationists are those who give five or six church-state
separationist responses and zero church-state integrationist responses. All
other respondents in the larger “church-state separationist” category are
classified as “moderate” separationists. See Methodology for
additional details.
Slightly fewer than one-in-five U.S. adults (18%) have mixed views –
expressing support for church-state separation on some of the survey’s
questions and support for increased church-state integration on about as many. And
one-in-eight offer no opinion on a majority of these questions. The survey shows, furthermore, that even in the groups that tend to
express the most support for the intermingling of church and state, the
“church-state integrationist” perspective is the exception, not the norm.
Among White evangelical Protestants, for example, fewer than half (36%)
express consistent support for a church-state integrationist perspective,
although this is larger than the share of White evangelicals who favor the
separation of church and state (26%). An additional 28% have mixed views. Hispanic Protestants (26%) are among the other groups whose sympathy
for church-state integration is higher than average. By contrast, a desire
for church-state integration is almost nonexistent among U.S. Jews (1%) and
the religiously unaffiliated (2%), who consist of those describing their
religious identity as atheist, agnostic or “nothing in particular.” Among
self-identified atheists and agnostics, fully 96% fall into the church-state
separationist category. Most Democrats and those who lean toward the Democratic Party (72%)
prefer church-state separation, compared with 38% of Republicans – although
even Republicans are more likely to express this view than to consistently
favor the integration of church and state (25%). The survey finds support for church-state integration is slightly
higher among White respondents (16%) than among Hispanic Americans (11%). But
at the same time, White people also are most likely to voice support for
church-state separation,
whereas Hispanic and Black Americans are more inclined than White adults to
express no opinion on these questions. The survey finds little difference on
these questions between U.S.-born adults and those born outside the U.S. Support for separation of church and state is slightly higher among
men than women; women are more likely than men to be in the “no opinion”
category. College graduates are far more supportive of church-state
separation than are those with lower levels of education. Similarly, young
adults (ages 18 to 29) are more likely than their elders to consistently
favor the separation of church and state. Support for separation of church and state is lower in the South than
in other parts of the country. Still, even in the South, fewer than
one-in-five people consistently express a desire for the integration of
church and state. A closer look at the church-state scale What, specifically, do people in each category desire in terms of the
relationship between church and state? On each of the six scale items, majorities
of those in the church-state integrationist category express support for the
intermingling of religion and government, ranging from 60% who say the
federal government should advocate Christian religious values to 88% who
favor allowing towns to exhibit religious displays and public school teachers
to lead Christian prayers. By contrast, most church-state separationists take
the opposite position on all six questions, ranging from 58% who say
religious displays should be kept off public property to 95% who say the
federal government should never declare any official religion. These patterns
are unsurprising, given the criteria for the categories. But those in the “mixed” category are perhaps more interesting. Most
people in this group say they think religious displays should be permitted on
public property (71%) and are comfortable with public school teachers leading
Christian prayers (60%). But far fewer think the government should stop
enforcing separation of church and state (39%) or that the U.S. Constitution
was divinely inspired (29%). And clear majorities say the federal government
should never declare an official religion (62%) and should advocate moral
values shared by many faiths (61%) rather than Christian values. Church-state views, or White Christian
nationalism? The questions in the new survey gauging American attitudes on
church-state issues are similar (but not identical) to questions used by
other scholars to measure what they call “Christian nationalism.”1 Research
on Christian nationalism shows that it is correlated with attitudes about
race, immigration, gender roles, the place of the U.S. in the world, and much
more. The new survey also finds a clear connection between views on
church-state issues and attitudes on many other social and political topics,
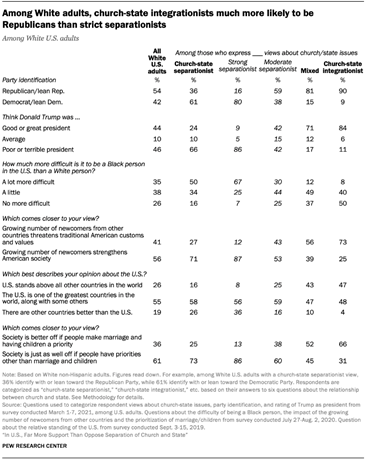
including matters of race and immigration. Most people who support separation
of church and state are Democrats or lean toward the Democratic Party, think
Donald Trump was a “poor” or “terrible” president, say immigrants strengthen
American society, and reject the notion that society is better off if people
prioritize getting married and having children. More than half of people with
a church-state separationist perspective say it is “a lot” more difficult to
be a Black person than a White person in the U.S., and that while the U.S. is
one of the greatest countries in the world, there are other countries that
are also great. By comparison, people who favor church-state integration are mostly
Republicans and Republican leaners, think Trump was a “good” or “great”
president, say the growing numbers of immigrants in the U.S. threaten
traditional American values, and feel that society would be better off if
more people prioritized getting married and having children. Church-state
integrationists are far more inclined than church-state separationists to say
that it is “no more difficult” to be Black than White in American society
(42% vs. 13%), and that the U.S. “stands above” all other countries (40% vs.
15%). These are just a few examples of the connection between church-state
views and attitudes about social and political issues. Similar correlations exist
between church-state views and responses to many other questions about race,
immigration, gender, and the place of the U.S. in the world. The data shows, furthermore, that these connections are at least as pronounced – if not
more so – among White Americans as among the public as a whole. White adults
with church-state integrationist views are much more likely than White
church-state separationists to say Trump was a good or great president (by a
margin of 59 percentage points), to identify with or lean toward the
Republican Party (by 54 points), to say that immigrants threaten traditional
American customs and values (47 points), and to say that society is better
when people prioritize getting married and having children (42 points). They
also are 35 points more likely to say that being Black is no more difficult
than being White in the U.S. today, and 32 points more likely to say the U.S.
has a unique place above all other countries in the world. These results are consistent with much of the existing research on
Christian nationalism, which demonstrates that among White people, Christian
nationalism is linked with support for the Republican Party, enthusiasm for
Trump, hostility toward immigrants and denial that racism is pervasive or
systemic in America. But the survey also shows that White church-state
integrationists are far from alone in their attitudes on these matters.
Indeed, majorities of
White people with “mixed” church-state views, as well as of those with a
“moderate” church-state separationist perspective, also identify with or lean
toward the Republican Party and view Trump as an average or
better-than-average president. And majorities of White adults in all three
categories (church-state integrationists, moderate church-state separationists,
and holders of mixed views on church-state questions) reject the idea that
being a Black person is a lot more difficult than being a White person in the
U.S. today. In fact, strong church-state separationists are the only group of White respondents who
are mostly Democrats, who mostly think Trump was a below average president,
and among whom a majority say being a Black person in the U.S. today is a lot
more difficult than being a White person. In other words, to the extent that
church-state views are connected with other social and political attitudes
among White respondents, those with the strongest church-state separationist viewpoint are in some
ways more distinctive from other White people than are those with
church-state integrationist views. A closer look at those with ‘no opinion’ on
church-state matters Roughly one-in-eight survey respondents (12% of all U.S. adults) are
categorized as having “no opinion” on the church-state scale, because they
say “neither/no opinion” or refuse to answer four (39%), five (30%) or all
six (31%) of the questions used to create the scale. This means the size of
the “no opinion” group is close to the size of the “church-state
integrationist” group (12% and 14%, respectively). So, who are the respondents in the “no opinion” category? Are they
really church-state integrationists but reluctant to express that point of
view in response to these questions? Are they church-state separationists who
are hesitant to share that opinion? Or are they people who are genuinely uncertain
about, unfamiliar with or uninterested in church-state issues? Of course, the survey cannot provide a direct answer because, by
definition, these respondents did not express a point of view – one way or
the other – on the church-state questions. However, those in the “no opinion”
category are distinctive in certain ways. Perhaps most obviously, they are
far less likely than the full sample of respondents to be college graduates
(15% vs. 33%), and far more likely to have a high school education or less
(56% vs. 36%). This is expected, since past research on patterns of survey
response has revealed that people with lower levels of educational attainment
are more inclined than those with higher levels of education to express no
opinion on many kinds of survey questions. Indeed, in addition to the
questions about church-state issues, the survey included 36 other questions
that were asked of the full sample of respondents; those in the “no opinion”
category decline to provide a substantive response to 3.9 of the 36
questions, on average, compared with 1.6 questions left with no substantive
response by respondents in other categories, on average. Compared with the full sample of respondents, those with “no opinion”
on the church-state scale also are less likely to be White, non-Hispanic
adults, and more likely to be Black or Hispanic. People in the “no opinion”
category also are a bit more likely to be under age 65 than are the full
sample of respondents. In terms of their political and religious profile, there is little
evidence to suggest that the “no opinion” category harbors a disproportionate
share of either “church-state integrationists” or “church-state
separationists.” Compared with the full sample of respondents, those in the
“no opinion” group are more likely than the full sample to identify as
political independents or with a third party and to decline to lean toward
either major party (15% vs. 5%), and also to describe themselves as
ideological moderates (50% vs. 38%). The religious profile of those in the
“no opinion” group closely resembles the religious profile of the full sample
of respondents. In addition to the six questions that make up the church-state issues
scale, the survey included a question that asked Americans which of two
statements comes closer to their own view: “God favors the United States over
all other countries,” or “God does not favor any one country over all the
others.” Overall, seven-in-ten U.S. adults choose the latter option: God does
not favor any one country. Just 5% of U.S. adults say they think God favors
the U.S. over all other countries, while 25% say neither, express no opinion
or decline to answer.2 The accompanying detailed tables provide
additional information about how social and demographic groups answered the
questions about church-state issues. (PEW) OCTOBER 28, 2021 714-43-15/Polls COVID-19 Vaccine Now Required For 36% Of U.S. Workers
WASHINGTON, D.C. -- The latest Gallup COVID-19 tracking survey finds
36% of U.S. employees saying their employer is requiring all its workers
without a medical exemption to be vaccinated against COVID-19. The percentage
has steadily increased each of the last three months, rising from 9% in July.
Line graph. Thirty-six percent of U.S. adults working full or part
time say their employer is requiring employees to get vaccinated against
COVID-19. The percentage is up from 29% in September and 19% in August. It
ranged between 5% and 9% from May to July. In addition to those saying their employer is mandating vaccination,
the Oct. 18-24 survey finds 39% of U.S. workers saying their employer is
encouraging but not requiring them. This percentage has declined from 62% in
July as those who say their employer requires vaccines has risen. Meanwhile, 25% of U.S. workers say their employer has not indicated a
vaccine policy, a proportion that has been relatively steady since Gallup
first asked the question in May. Employees Continue to Support Mandates More U.S. employees say they favor mandates (56%) than are opposed to
them (37%). The percentage in favor has grown from 46% in May, while there
has been little change in the percentage opposed. Fewer today than in May (7%
vs. 15%, respectively) say they neither favor nor oppose vaccination
requirements. U.S. Workers' Opinions on Employer Vaccination Requirements How would you feel about your employer requiring all employees (who
do not have a medical exemption) to receive the coronavirus/COVID-19
vaccination?
Most U.S. workers hold strong opinions on vaccination requirements. A
combined 75% either strongly favor (45%) or strongly oppose (30%) them. In
May, 60% of workers had strong opinions in either direction. Back then, those
with strong opinions were equally likely to favor as to oppose vaccine
requirements, 29% to 30%. The growth since May, then, has come in the
percentage who are strongly in favor. Will Vaccine Policy Cause Workers to Look
for New Jobs? A key concern for employers is whether vaccine requirements will
cause employees to leave their organization to find a job with a COVID-19
vaccination policy that matches their personal preferences. Nearly one in three U.S. workers are poised to look for a new job if
their employer sets a policy on COVID-19 vaccinations with which they
disagree. This includes 16% who are strongly opposed to vaccination
requirements and 15% who are strongly in favor of them, determined as
follows:
Those figures are likely upper bounds of potential job losses tied to
COVID-19 vaccine policy, as many will find themselves in sync with their
employers' stance -- or not follow through and leave their job even if they
disagree. For example, some workers strongly opposed to vaccination requirements
may ultimately decide to get vaccinated in order to keep their job. Also,
some workers concerned about COVID-19 transmission at work may decide to stay
at their job even if their employer does not mandate vaccinations for all
workers there. A separate question in the survey finds that 7% of workers who
strongly oppose employer vaccine requirements are actively looking for a
different job. The question does not assess whether the job search is related
to COVID-19 or for other reasons. Likewise, 10% percent of workers strongly
in favor of COVID-19 vaccine requirements are actively looking for a
different job. Notably, neither figure is meaningfully different from the 7% of all
U.S. workers who say they are currently actively looking for a different job. Decisions about leaving one's job are most relevant to those working
at organizations with vaccination requirements in place. The Gallup data
indicate that 3% of workers do not plan to get vaccinated and work for an
employer that has a vaccination requirement in place right now. Another 2%
who work for employers with vaccination requirements are currently
unvaccinated but plan to be. Though inconclusive due to small sample sizes, combined data from
September and October indicates that unvaccinated employees who work for an
employer requiring vaccination are much more likely than other workers to be
searching for a job. The data suggest that these employees are two to three
times more likely than other workers to be actively looking for another job. About One in Five Workers Are Unvaccinated The vast majority of U.S. workers will not have to choose between
getting vaccinated or losing their job if their employer mandates COVID-19
vaccinations. Seventy-five percent of U.S. adults employed full or part time
are vaccinated, and another 5% say they plan to be. That leaves 21% unvaccinated according to combined data from the
September and October surveys, which is down from 31% in January, when Gallup
first measured vaccination status, and 24% in August. Notably, vaccination rates lag most among blue-collar workers, among
whom 56% are currently vaccinated, 5% plan to be and 38% do not intend to get
vaccinated. The vaccination rates among white-collar, education and
healthcare workers all exceed 80%. Worker Vaccination Status, by Job Area
Bottom Line The Biden administration's workplace rules were announced in
September, and many employers that did not already have vaccination
requirements of their own in place have begun to comply with those. Legal
challenges to government and employer vaccine mandates are working their way
through the court system, but as those get sorted out, an increasing number
of U.S. workers say their employer is requiring its employees to get COVID-19
vaccines. Most American workers favor these, but a consistent 30% are strongly
opposed. Those workers, some of whom are vaccinated but many who are not, are
likely to indicate they will look around for a different job if employers
require them to be vaccinated. This group represents about 15% of all U.S.
workers, and about half of these, 7%, say they are actively looking for a
different job. But a smaller percentage of workers, 3%, have no plans to be
vaccinated and work for an employer who currently has a vaccination
requirement in place. Most workers are still not employed by organizations that require
COVID-19 vaccinations, so many workers are not yet grappling with an employer
mandate to be vaccinated. Some may never confront that situation, even if the
Biden administration's actions are upheld in the courts, if those workers are
employed by an employer beyond the reach of the federal mandates. Whether tied to COVID-19 vaccination requirements or other factors, a
record number of U.S. workers are quitting their jobs, according to the
Bureau of Labor Statistics. Though the percentage of U.S. workers who choose
to leave their employer over vaccination requirements may ultimately be
small, employers may still be negatively affected if they struggle to find
replacement workers when many organizations are having difficulty filling
needed jobs. (Gallup) OCTOBER 29, 2021 Source: https://news.gallup.com/poll/356786/covid-vaccine-required-workers.aspx AUSTRALIA
714-43-16/Polls Paypal Is The Clear Leader With 72.5% Of Australians Aware Of The
Platform
Of the four leading online payment platforms PayPal is the clear
leader with 72.5% of Australians aware of the platform. This compares to just
under a quarter, 23.6%, that are aware of Visa Checkout, and just under
one-in-six aware of Western Union (16.4%) or masterpass (16.3%). The COVID-19 pandemic has provided a huge boon to online retailers,
and this has also driven the increased usage of online payment platforms such
as PayPal. Now 47.3% of Australians have used PayPal in the last 12 months,
up nearly 10% points from 37.8% in February 2020 just before the pandemic hit
Australia – reversing the trend. Usage of PayPal had been at 40.5% of Australians in January 2018 and
gradually increasing before peaking at 42% in June 2018. From mid-2018 usage
of PayPal had begun to gently decline as newer forms of payment such as
buy-now-pay-later services gained an increasing share of the digital payment
market. Over three-quarters of Australians, 16.5 million (78.1%), are now
aware of buy-now-pay-later services such as Afterpay, Zip, Latitude Pay and
Humm. However, usage of these services is far lower with only 3.5 million
Australians (16.6%) using a buy-now-pay-later service in the last 12 months. To learn more about how Australians are using ‘buy-now-pay-later’
services please see our recent release on trends in that market: ‘$39
billion purchase of Afterpay highlights value of buy-now-pay-later services
such as Zip, Humm and Latitude Pay’. These new digital payment findings are from Roy Morgan Single Source,
Australia’s leading consumer survey, derived from in-depth interviews with
around 50,000 Australians annually. Online payment platform usage trends (used
in last 12 months): 2018-2021
Roy Morgan CEO Michele Levine says the
COVID-19 pandemic has had many impacts throughout the economy and one of the
most prominent is the increase in online retail sales – which has had a large
positive impact for online payment platform PayPal: “The proliferation of digital payment
services in recent years is profoundly changing the way Australians conduct
financial transactions and pay for goods and services. “Often referred to as ‘fintech’ – the union
of finance with technology – these new services include buy-now-pay-later
services led by Afterpay, contactless/cardless mobile payment services such
as Apple Pay or Google Pay, wearable payment devices such as fitbit pay,
banks own mobile payment services such as Commbank Tap & Pay and even
cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. “However, despite the multitude of options now
available for consumers PayPal stands out as the leading digital online
payment platform used by 47.3% of Australians in the last 12 months. PayPal
is ahead of second-placed bill payment service BPAY used by 42.7% of people
largely to pay bills and both are well ahead of third-placed Afterpay used by
13% of Australians. “The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in
March 2020 drove people to purchase goods online and led to a steep increase
in people using the PayPal online payment platform which increased by nearly
10% points since February 2020. This is the largest increase during the
pandemic for any of the many digital payment services now available. “As a more established digital payment
service PayPal has been facilitating the online purchase transactions of
Australians for nearly twenty years. This longevity in the market leads to
high penetration for PayPal amongst key demographic groups – over 55% of
people aged 35-49 used PayPal in the last 12 months – higher usage than any
other age group. “The annual Roy Morgan forecasts on pre-Christmas retail
spending released in conjunction with the Australian Retailers Association
(ARA) last week show Australians are set to spend $58.8 billion in the pre-Christmas period this year –
virtually unchanged from the record spending a year ago. “Importantly for online digital platforms
such as PayPal, a recent Roy Morgan survey showed Australians are predicting
an average of 48% of their Christmas gift shopping will be done online. “These results show the next few months are
set to break new ground with a record level of online sales and heavy
utilisation of digital payment services. PayPal has been a big winner of the
move to online so far during the pandemic and over the next few months we
will be keeping a close eye on whether PayPal can hold onto the gains it has
made over the last 18 months or whether rival digital payment services such
as Afterpay can close the gap as we enter ‘COVID-normal’.” (Roy Morgan) October 26 2021 Source: https://www.roymorgan.com/findings/8831-digital-payment-solutions-october-2021-202110260410 714-43-17/Polls ALP (54%) Increases Lead Over The L-NP (46%) As The Federal
Government Discusses “Net Zero” Carbon Dioxide Emissions
ALP support has increased to 54% (up 1% point since mid-October) cf.
L-NP on 46% (down 1% point) on a two-party preferred basis according to the
latest Roy Morgan Poll on Federal voting intention conducted over the last
two weekends. The 1% point swing to the ALP came after the governing Liberal and
National parties have spent the last few weeks ‘haggling’ about a change in
policy for the Government to support a target of “Net Zero” carbon dioxide
emissions for Australia by 2050. The Liberal Party under the leadership of Prime Minister Scott
Morrison has been pushing to be able to make this commitment at the upcoming
United Nations Climate Change Conference in Glasgow, Scotland whereas the National
Party has resisted the reform. The latest news over the weekend is that the
National Party has voted narrowly to support this reform although clear
divisions remain within the party with at least one National Party Senator
vowing to campaign against the change. Government support weakens in Queensland
and NSW over the last two weeks The arguing between the Liberal and National parties regarding the
Government’s policy on carbon dioxide emissions targets has been most intense
in Queensland and although still leading, the LNP has lost support. In
Queensland the LNP is now on 51.5% (down 3.5% points since mid-October) cf.
ALP 48.5% (up 3.5% points) on a two-party preferred basis. Despite the LNP’s
lead this represents a swing of 6.9% points to the ALP since the 2019 Federal
Election. In NSW former Premier Gladys Berejiklian, who resigned in early
October, has been questioned by ICAC – the Independent Commission Against
Corruption over the last few weeks over her relationship with former State MP
Darryl Maguire. Berejiklian is the third Liberal Premier in NSW to resign
amidst allegations of corruption. The scandal surrounding Berejiklian has certainly hurt the Liberal
Party and the ALP has increased its lead in NSW over the last two weeks with
ALP support now up 2% points to 55.5% cf. L-NP on 44.5% (down 2% points) on a
two-party preferred basis. This result represents a swing of 7.3% points to
the ALP since the 2019 Federal Election. If a Federal Election were held now the ALP would be elected with a similar
margin to that won by John Howard at the 1996 Federal Election (ALP 53.6% cf.
L-NP 46.4%). This Roy Morgan Poll on Federal voting intention and Roy Morgan
Government Confidence was conducted via telephone and online interviewing
last weekend. Roy Morgan interviewed 2,778 Australian electors aged 18+ on
the weekends of October 16/17 & 23/24, 2021. A higher than usual 8% of
electors (up 0.5% points from mid-October) can’t say who they support. Primary Voting Intention dropped for both
major parties in October, but up for the Greens Primary support for the L-NP was down 1% point to 36.5% in October
and is still ahead of the ALP which was also down 1% point to 35%. In contrast to the two major parties, Greens support increased by 2%
points to 13.5% as media attention in October turned to Australia’s response
to global warming and climate change. Support for One Nation was up 0.5% points to 3.5% while support for
Independents/Others was down 0.5% points to 11.5%. Voting analysis by State shows the ALP leading on a two-party
preferred basis in four States including Victoria, New South Wales, Western
Australia and Tasmania. In contrast, the LNP leads only in Queensland and
South Australia. The ALP leads in Victoria on 56.5% (up 0.5% points since mid-October)
compared to the L-NP on 43.5% (down 0.5% points) on a two-party preferred
basis. This result represents a swing of 3.4% points to the ALP in Victoria
since the 2019 Federal Election. The situation in Western Australia is unchanged with the ALP on 55%
(unchanged since mid-October) well ahead of the L-NP on 45% (unchanged) on a
two-party preferred basis. This result reprensents a massive swing of 10.6%
points to the ALP since the 2019 Federal Election. The L-NP has regained the lead in South Australia with a significant
increase in support with the L-NP 51.5% (up 6% points since mid-October) now
ahead of the ALP on 48.5% (down 6% pointws) on a two-party preferred basis.
This represents a swing of 2.2% points to the L-NP since the 2019 Federal
Election. The ALP continues to enjoy a strong lead in Tasmania with the ALP
58% cf. L-NP 42% - a swing of 2% points to the ALP since the 2019 Federal
Election. Roy Morgan Government Confidence increases
by 3pts to 98 The Roy Morgan Government Confidence Rating has increased by 3ps to
98 in late October. Now 41% (up 1% point) of Australians say the
country is ‘heading in the right direction’, while 43%, down 2% points, say
the country is ‘heading in the wrong direction’. However, there remains a wide divergence of over 30pts between
different States with Government Confidence above 100 in three States
(Western Australia, Queensland and New South Wales) and below the neutral
level of 100 in the three other States (Victoria, Tasmania and South
Australia). Government Confidence is highest in Western Australia at 110.5 in
late October while the measure is also in positive territory in both
Queensland at 103 and New South Wales at 101. New South Wales finally emerged
from a more than 100-day lockdown during mid-October. In contrast, Government Confidence is below the neutral level of 100
in Victoria at 90 in late October. Victoria’s sixth lockdown ended towards
the end of the interviewing period and restrictions are set to ease further
over the next few weeks as the vaccination rate continues to increase. Government Confidence is also below the neutral level of 100 in South
Australia at 94 in late October. South Australia is one of only two States
yet to outline when it plans to re-open to all of Australia. Government
Confidence is lowest of all in tourism-dependent Tasmania at 75. The
Tasmanian Premier finally announced last week that the State would re-open to
all of Australia on December 15. Michele Levine, CEO, Roy Morgan says the
ALP increased its lead as the L-NP Government spent much of the last two
weeks engaged in internal arguments about whether Australia should pursue a
policy of ‘Net Zero’ carbon dioxide emissions by 2050: “Today’s Roy Morgan Poll on Federal voting
intention shows the ALP 54% (up 1% point since mid- October) increasing its
clear election-winning lead over the L-NP 46% (down 1% point) on a two-party
preferred basis. “However, the major beneficiary over the
last two weeks has been the Greens which increased their support by 2% points
to 13.5% at the expense of both major parties amidst heavy discussions about
Australia’s response to Global Warming and Climate Change. “This week the Federal Government finally
came to an agreement with the National Party signing on to commit to the goal
of ‘Net Zero’ carbon dioxide emissions by 2050. Although the L-NP Government
has now committed to reducing Australia’s carbon dioxide emissions to ‘Net
Zero’ by 2050, they have refused to modify their targets for reducing
emissions by 2030. “Australia signed an agreement in Paris in
2015 to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 26-28% by 2030 and the indications
are that Australia will exceed this target and emissions will be reduced by
30-35% on current trajectories. Based on these forecasts the ALP, and also
the Greens, are calling for the Government to set larger targets to meet for
reducing carbon dioxide emissions. “The ALP has not put a figure on their 2030
emissions reduction target but the Greens are arguing for carbon dioxide
emissions to be reduced by 75% by 2030 and for Australia to reach ‘Net Zero’
emissions by 2035 – 15 years earlier than the Federal Government’s new
commitment. “For voters who regard the issue of Global
Warming and Climate Change as more important than any other the Greens are
the party that is most committed to acting now and acting fast. A special Roy Morgan survey of Australians
conducted in September found
24% of Australians regard Environmental problems such as Global Warming and
Climate Change as the most important problems facing Australia – second only
to COVID-19 related issues (36%). “On a State-based level the ALP has gained
ground over the last two weeks in both Queensland and NSW. The arguments in
Queensland surrounding the Federal Government’s policies on reducing carbon
dioxide emissions have been heated with the State heavily reliant on resources
such as coal. Despite this the LNP holds a slim lead in Queensland: LNP 51.5%
cf. ALP 48.5%. “However in NSW the resignation of former
Premier Gladys Berejiklian in early October, and her appearance before the
Independent Commission Against Corruption (ICAC) over the last few weeks, has
clearly hurt the Liberal Party in NSW. The ALP has increased its lead in NSW
and now leads comfortably in the key State: ALP 55.5% cf. L-NP 44.5%. “The next Roy Morgan Poll on Federal voting
intention due in two weeks will be a big indicator for how well the
Government’s new policy for pursing ‘Net Zero’ carbon dioxide emissions by
2050 has been regarded by the electorate.” Electors were asked: “If an
election for the House of Representatives were held today – which party will
receive your first preference? and “Generally speaking, do you feel that things in
Australia are heading in the right direction or would you say things are
seriously heading in the wrong direction?” For further information:
Australian Federal Voting Intention:
Two-Party Preferred (2019-2021)
(Roy Morgan) October 27 2021 Source: https://www.roymorgan.com/findings/8832-federal-voting-intention-october-2021-202110270611 MULTICOUNTRY
STUDIES
714-43-18/Polls Positive Impact Of Intersectionality In Advertising In 4 Countries
The report examines the impact
of intersectionality in advertising across four countries
(Japan, Turkey, the United Kingdom, and the United States) revealing that advertising that represents people
across a variety of social categorizations resonates with all consumers.
This marks the second instalment of the ‘Beyond Gender' study; the first
report released in 2018 centred on how gender intersects with cultural
contexts and forms of discrimination in Brazil, India, and South Africa.
Convened by UN Women, the Unstereotype Alliance is a thought- and action
platform that seeks to eradicate harmful stereotypes from advertising and
media. Sara Denby, Head of the Unstereotype
Alliance Secretariat, UN Women, said: “This unique study not only demonstrates that advertising has the
ability to drive positive social change, but that fully representative and
inclusive portrayals of people in all their unique complexities is good for
business in every market." The distinct
findings across the countries underscore the importance of approaching
intersectionality through a culturally-nuanced lens, both in terms of
representation and the consideration of people’s experiences and feelings in
each community. The new research found that intersectional advertising grows and
deepens consumers' ties with a brand. The inclusion of progressive and
intersectional portrayals of people drives their feelings of “closeness” with
a brand – an indicator of brand performance – with a significantly acute
impact on under-represented and traditionally marginalized communities. Whilst intersectionality in advertising may be seen as only affecting
a small or targeted group of people, the research illustrates its impact can
be far greater. Many consumers state they do not see themselves in
advertising and struggle to find products that feel as though they’re made
for them – confirming the shift to more representative content is not just
the right thing to do, but also a business imperative. Philip Thomas, Chairman, LIONS said:
“Lions supports these initiatives, firstly
because they raise awareness of the issues facing our industry and secondly -
and perhaps more importantly - because they offer best practice guidance on
how we can drive change and progress. Intersectionality
in advertising is an incredibly important area of focus; it supports the full
and true representation of people’s lived experiences It’s our hope that people actively engage
with the findings of this research and the importance of an intersectional
approach so that we see more progressive and representational advertising
reflected back.” Kaitlin Love, Vice-President, Ipsos said:
“Across the industry, consumers feel that
brands lag behind the rapid demographic and normative shifts happening in
society." This
groundbreaking research shows that brands only stand to benefit from taking
an intersectional approach in their advertising. Some overall highlights from the report include:
(Ipsos Denmark) 25 October 2021 Source: https://www.ipsos.com/en-dk/positive-impact-intersectionality-advertising 714-43-19/Polls The Proportion Saying COVID One Of The Biggest Issues Facing Their
Country Has Fallen From 36% To 29% (Global Country Average) Since September
Within 28 Countries
After 18 consecutive months of our What Worries the World survey
showing Coronavirus to be the biggest concern for people across 28 countries,
October 2021 marks the first significant change in our issues ranking. COVID-19 falls to (joint) third position,
with the average proportion worldwide who count one of the biggest worries in
their country today falling 7 points to 29% compared to the previous month’s
results. In its place, Poverty and
social inequality becomes the number one issue globally. One-third
(33%) on average select this – a slight increase of 2 percentage points since
last month. Unemployment is the second biggest worry (30%), just ahead of
COVID-19 and Financial/political corruption (both at 29%).
Before our survey began tracking levels of concern about Coronavirus
alongside our other regular issues, Poverty and social inequality was a
dominant concern, coming either first or joint-first for the earlier months
of 2020. Hungary and Russia are the countries ranking highest in terms of
concern about poverty and social inequality, with the issue highlighted by
55% in each; they are followed by Colombia (47%) and Brazil (46%). Compared to last month, 19 countries show rising concern about this
issue – most of all in Hungary, Brazil, Japan, and Peru, which all record
6-point increases. It becomes the top concern (replacing COVID-19) in France, Germany,
and Japan this month. Unemployment (30%) Unemployment is the second greatest worry worldwide, with three in 10
(30%) on average counting it as one of the most important issues facing their
country today. South Africa is once again the country most concerned about
unemployment and jobs as two-thirds (67%) select this as a top worry. Next in
the list, with around one in two concerned about jobs, are Spain (54%), Italy
(51%) and Colombia (50%). The largest increases in concern on this issue since last month are
seen in Saudi Arabia (+8) and Turkey (+7). On the other hand, it falls by 7
points in Australia and 6 points in Canada. Coronavirus (29%) A 7-point decrease in the global country average score for
Coronavirus this month sees what had been the world’s top concern for 18
months fall to joint-third position in our issues ranking. On average, 29%
say this is one of the top issues facing their country today (level with
corruption). Despite a 10-point drop over the month, Malaysia remains the most
concerned about COVID-19 today with 64% selecting the issue. Japan falls to
third most concerned this month with a drop of 22 points 50%, putting it
behind Australia (-6 to 52%). We see other significant decreases in the proportion of the public
saying Coronavirus is a top issue in Mexico (-16), Germany (-14), Peru (-12)
and Brazil (also -12). Only one country registers a significant increase in concern about
Coronavirus this month – Russia (+5 to 22%). Just four countries have Coronavirus as their top concern in October
(Australia, Great Britain, Malaysia, and the US), down from a total of 12 in
September and 24 in April 2020.
With 29% on average across all countries saying that
Financial/Political corruption is an important issue for their country today,
this ranks as the third greatest concern – level with COVID-19. South Africans show the highest levels of concern (55%), followed by
Colombia (52%) and Malaysia (50%). One in two also select this as a key worry
in Hungary and Peru (49% in both). The biggest increase in the proportion selecting this issue is +12
points in South Korea. The percentages concerned in Peru and Saudi Arabia
also grow by 8 points. Corruption is the number one concern in Colombia and Peru today. Crime and violence (27%) Crime & violence is considered one of the most important issues
today by an average of 27% of people across all countries surveyed, making
this our fifth greatest worry. The top three countries most concerned about crime and violence are
Sweden (68%), Mexico (56%), and South Africa (54%). This is the top issue for
these first two countries, while South Africa is relatively more concerned
about unemployment and corruption. Crime also ranks as the most worrying issue for people in Israel
(which sees a 13-point increase since last month to 45%) and Chile (at 41%,
level with last month). Sitting between these two countries, with 43%, is
Colombia, where there has been a 7-point month-on-month increase in concern
about crime and violence. Climate change (16%) With the landmark UN Climate Change Conference taking place in
November, we take a look at the latest figures on global concern about
climate change. Across all countries, 15% on average consider climate change to be
one of the most worrying topics in their country today. Levels of concern rise to 34% in Canada and Germany. This represents
the highest level of reported concern about climate change seen in Canada to
date. Close behind, with three in 10 considering putting climate change in
their top worries, are Australia (31%) and the Netherlands (30%). This month, climate change ranks 10th in the full list of 18 issues,
just behind education, taxes, and inflation, all at 16%.
Across the 28 nations surveyed, 64% on average say that things in
their country are on the wrong track while 36% think they are heading in the
right direction – little changed from previous months. This shows falling
levels of concern about Coronavirus have not necessarily impacted the
positivity of the public’s outlook. Colombia is the country where most people say that things are heading
in the wrong direction (90%), followed by Peru (83%), Argentina (82%), and
Brazil (80%). There has been a surge of optimism in Malaysia since last month (+16
saying things are heading in the right direction). Other shifts towards an
optimistic view of the road ahead are seen in Japan (+8) and Hungary (+7). Meanwhile, there has been a 7-point drop in both Sweden and Saudi
Arabia – although Saudi Arabia still retains its too spot as the country most
positive about its direction of travel. (Ipsos MORI) 26 October 2021 Source: https://www.ipsos.com/ipsos-mori/en-uk/what-worries-world-october-2021 714-43-20/Polls About A Third Of Consumers In The UK (35%) And About A Quarter Of
Those In The US (27%) Say The Processor Brand Is Important To Them When
Buying A Laptop
Announcing the new MacBook Pro line of notebooks this month,
Apple explained at great length the virtues of its new M1 Pro and M1 Max chips.
As Apple continues its transition to its in-house silicon, a YouGov survey in
the US and the UK reveals just how much importance consumers place on what
brand of chip is found in their laptop. About a third of consumers in the UK (35%) and about a quarter of
those in the US (27%) say the processor brand is important to them when
buying a laptop. Those figures are higher among those who use laptops for
creative work (39% in the US, 43% in the UK) or for gaming (53% in the US,
52% in the UK).
Ports, ports, ports: The latest generation of MacBook Pros
also feature something users have been begging for years: Ports. HDMI,
USB, and an SD card slot all made a return to the notebook after Apple did
away with them in 2016 in pursuit of a slimmer form factor. Our survey shows such ports are as important – if not more important
– than the branded chip powering the device, particularly among those doing
creative work or general office work. The new slate of MacBook Pros come in 14-inch and 16-inch
versions, which hits the sweet spot for consumers. A plurality of consumers
(43% and 39% in the UK) says 15 to 16 inches in the ideal size, while the 13-
to 14-inch range is the next most popular (31% in the US, 35% in the
UK). Will consumers buy? So, Apple seems to have struck a lot of
right chords with its latest offering. It has existing Mac owners excited,
with 28% of MacOS users in the US – and 25% in the UK – likely to pick one up
in the next 12 months. Is it enough to woe Windows loyalists? Not in great
quantities, but 6% of those users in US and 6% in the UK say they’re likely
to pick up a MacBook Pro in the next year. Apple’s Airpods have become the brand’s hottest item. According
to a recent international survey conducted in 17 markets by
YouGov, it’s among the most coveted tech gadgets this holiday season.
Riding on that success, Apple unveiled the third generation of wireless
earphones, which now feature spatial audio, water resistance and a redesigned
form factor. In the US, 16% of Americans say they’re likely pick up a pair in
the next three months, and 9% of Brits say so. The importance of the ecosystem: Part of the success
of AirPods can be attributed to how well they seamlessly integrate with
iPhones, which remains by far the most important product in Apple’s lineup.
Apple goes to great lengths to ensure their hardware can be used with one
another to create the so-called “walled-garden,” a tech ecosystem that makes
life easier and easier the more a consumer buys in. While it may be construed
as a negative by some industry observers - since it’s hard to escape the
ecosystem once invested - survey data shows roughly a third of consumers say
it’s important to them that their personal devices are the same brand. Survey
data shows this is enormously true among Mac users (79%), but not as much in
the Windows camp (17%). (YouGov UK) October 26, 2021 714-43-21/Polls Young Urban Indian Males Are The Most Likely To Follow Gaming
Influencers, Survey Conducted In 17 Markets
YouGov’s new gaming report shows that a quarter of young urban Indian
males between 18-34 years follow gaming influencers in India. YouGov’s International Gaming Report 2021 is
a three-part series on the global gaming influencer landscape. Part 1 sizes
the gaming influencer global fanbase across 17 international markets
and reveals where these influencer followers sit within the global influencer
sector as a whole. When it comes to the type of influencers followed among adults of all
ages, data suggests that just under one in ten (9%) consumers across all 17
markets follow gaming influencers. However, this changes significantly when
we look at different demographic groups. Globally, gaming influencers are the
most popular type of influencer followed by males aged 18-34 years, with
almost a quarter (23%) of all adults in this demographic segment following
gaming personalities. The proportion is higher in Asian countries, with Hong Kong (42%) and
Indonesia (36%) reporting the highest numbers within this cohort. In India, about a fourth (25%) seem to be following gaming influencers,
which is higher than the proportions in the UK (11%) and US (19%).
When it comes to gaming frequency, YouGov data shows 68% of
adults across the 17 international markets surveyed currently game at least
once a week. The global proportion of those following gaming influencers
increases from 9% overall to 15% among active gamers (playing video games 1+
hours per week), and to 20% among heavy gamers (playing video games 11+ hours
per week).
India stands out from the rest of the world with the highest
penetration of gaming influencer followers both among active gamers (25%) as
well as heavy gamers (33%). India is closely followed by Indonesia and China,
reporting high numbers for gaming influencer followers in both groups. The lowest
numbers are reported by Denmark, where only 11% of heavy gamers & 7% of
active gamers follow gaming influencers. While fans of gaming influencers are heavily invested in gaming, they
also have a wide variety of other entertainment interests. In India, the top
‘other influencer’ categories followed by gaming influencer fans include
health (59%), fitness (54%), sports (53%) and food (52%). This presents an
opportunity for brands, advertisers, and sponsors who are keen to engage this
audience through outside of the gaming landscape.
(YouGov India) Source: https://in.yougov.com/en-hi/news/2021/10/27/young-urban-indian-males-are-most-likely-follow-ga/ 714-43-22/Polls UK Public Highly Supportive Of COP26 Goals Among G20 Countries But
Few Expect The Government To Take The Steps Needed
New research by Ipsos MORI shows there is more to be done by the UK
in the fight against climate change, with the UK public not convinced of the
country’s ability to deliver on climate and wanting to see more action. In a survey of 9,999 UK adults aged 16+, three-quarters (76%) agree
the UK should do more to combat climate change. However, ahead of COP26,
there is low confidence that the government will deliver on climate, as over
half (55%) are not confident that the government will take the actions needed
to help combat climate change within the next few years (40% are
confident). Despite this, the UK public sees the country as a ‘climate hero’ in
the G20, as the UK came highest when people were asked to say which countries
across the G20 were doing most to tackle the issue. 36% chose the UK,
followed by Germany (25%) and Canada (16%). On the other hand the main
‘climate villains’ across the G20 were seen as China (57%), the US (36%) and
India (26%), as these are considered to be the countries doing least to help. Almost two-thirds (63%) of UK adults say it is right that developed
countries who have contributed most to the climate emergency by producing the
most carbon emissions should pay more to solve the problem, and only 17%
disagree. The UK government recently announced it would double climate
finance aid over the next 5 years to £11.6 billion, and there is broad
support for this policy. A third of the UK public this is about right (37%)
and 21% think the amount should be increased. Only 17% think it is too
much and 10% that we shouldn’t be providing foreign aid to help tackle
climate change at all. Looking to the next few years, almost 7 in 10 (68%) feel confident
that they themselves will be able to take actions or make changes in their
lifestyle to help combat climate change. Only 22% are not confident. There is
also broad consensus that further action is needed, as only 5% cent say they
already take enough action, and 2% believe no action is needed. Despite widespread confidence in themselves, UK adults are much less
likely to have faith in others. Only 38% are confident that citizens/members
of the public in the UK will take the actions needed to help combat climate
change within the next few years. Similarly, only 37% are confident that
businesses in the UK will take the actions needed. There is strong support for the COP26 goals, with those related to
protecting and restoring forests and nature most strongly supported. More
than 9 in 10 (92%) support reducing the amount of deforestation and
protecting rainforests and other natural forests while 91% are in favour of
protecting and restoring nature (e.g. forests, rivers, oceans, natural
habitats). Only 1% oppose each of these goals. Most of the approaches given in the survey receive support from
a majority of Britons. Nearly 9 in 10 (88%) support encouraging investment in
renewable energy sources while 87% support making changes to protect
communities from the impacts of climate changes and 80% support speeding up
how quickly countries are moving away from coal-powered stations. Seventy-nine
per cent support getting countries to sign up to ambitious targets to reduce
their carbon emissions and three-quarters (74%) support encouraging rich
countries to provide financial help to developing countries to combat climate
change. While still receiving majority support, speeding up the switch to
electric vehicles is the most polarising goal, with 61% supporting this goal,
but 18% opposing it. Bridget Williams, Research Director at
Ipsos MORI said: While the public is currently unsure that
the Government will take the steps required to tackle climate change in the
UK, the Government can take heart from the very strong levels of public
support for the goals of the upcoming COP26 summit, and for policies
supporting developing countries in the fight against climate change. (Ipsos MORI) 28 October 2021 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||